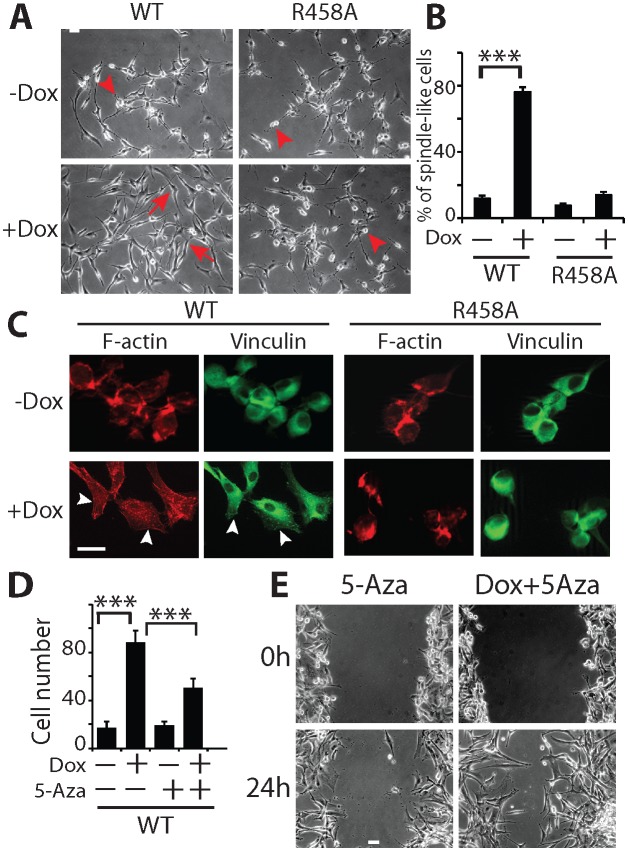
Figure 2. KLF4 WT-induced cell migration is methylation dependent.
(A) Expression of KLF4 WT but not R458A induced cell morphology changes in U87 cells (+Dox, 48 hr). The control and R458A expressing cells showed round and short cell body (arrowheads), whereas KLF4 WT induced elongated, spindle-like cell shape (arrows). Bar = 25 µm. (B) Quantification of cell morphology changes after Dox treatment for 48 hr. More than 80% of the KLF4 WT expressing cells showed elongated, spindle-like cell morphology, whereas most KLF4 R458A expressing cells remained as round and short cells. (C) F-actin and vinculin staining in control, KLF4 WT and R458A-expressing cells. KLF4 WT induced actin stress fiber formation and focal adhesion formation (arrowheads). Bar = 10 µm. (D) Pre-treatment of the cells with DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-Aza (1µmol/L, 10 days) blocked KLF4 WT-induced cell migration in transwell assays. (E) Scratch assays indicating that 5-Aza blocked wound healing induced by KLF4 WT. Bar = 25 µm. ***p<0.001.