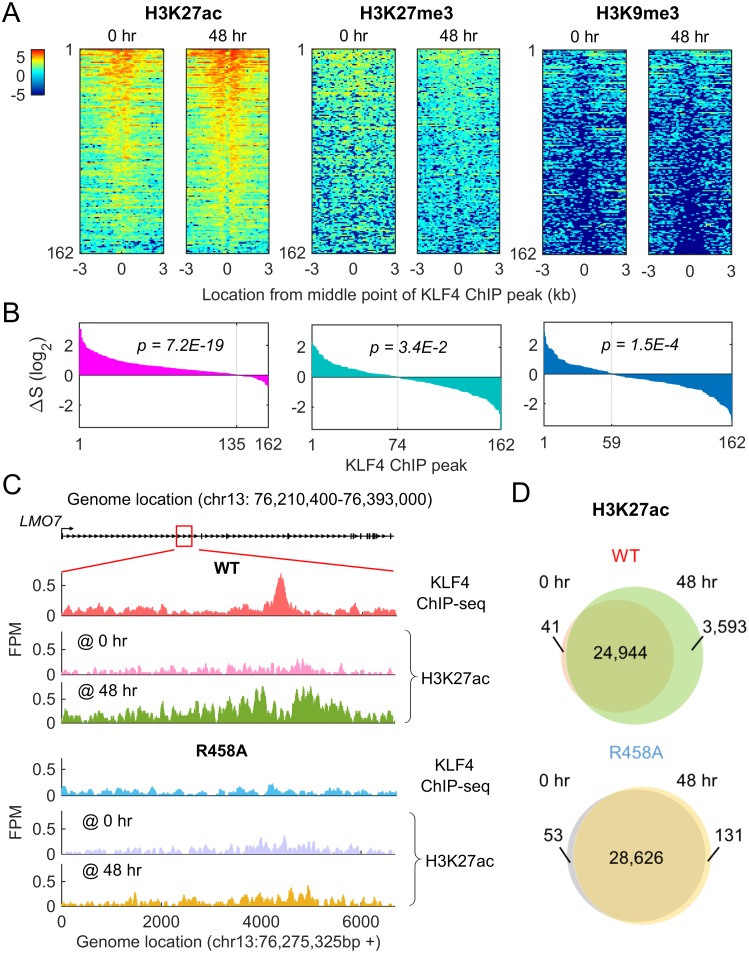
Figure 6. Methyl-mCpG dependent KLF4 binding activity triggers chromatin remodeling to activate gene expression.
(A) Heatmaps of histone mark signals, H3K27ac, H3K27me3, and H3K9me3, before and after KLF4-mCpG interactions (0 vs. 48 hr), respectively, ±3 kb surrounding 162 KLF4 ChIP peaks, which were associated with the 116 KLF4-mCpG direct targets. The peaks were sorted by their average signals at 48 hr for each histone mark. (B) The signal difference of histone marks between 48 hr and 0 hr, sorted from minimum to maximum. Over 83% of the 162 peaks had increased H3K27ac signals (p=7.2E-19), whereas 54.3% (p=3.4E-2) and 63.6% (p=1.5E-4) of the peaks had decrease in H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 signals, respectively. (C) Stronger H3K27ac signals were accumulated surrounding the KLF4 WT ChIP-seq peak on gene LMO7, at 48 hr after KLF4 WT induction; whereas no significant change in H3K27ac signals was observed in R458A expressing cells, as the R458A mutation abolished KLF4-mCpG binding ability. (D) Genome-wide analysis of dynamic changes of H3K27ac peaks before and after KLF4 WT or R458A induction, respectively. A total of 3593 new H3K27ac peaks appeared after KLF4 WT induction (upper panel), whereas only 131 new peaks were generated in KLF4 R458A expressing cells (lower panel), indicating that mCpG-dependent KLF4 binding activity caused chromatin remodeling to activate gene expression.
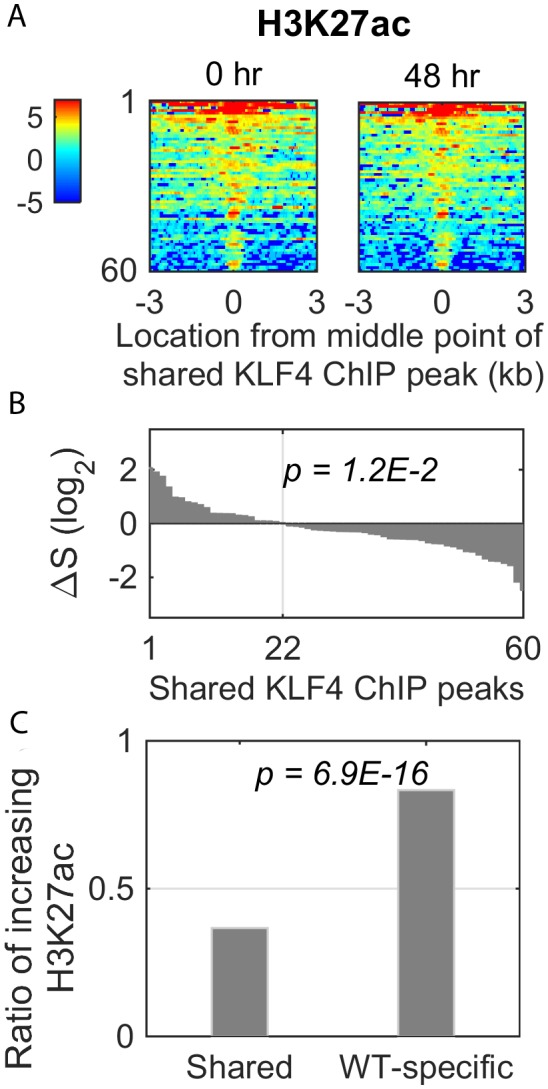
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Dynamic changes of histone mark H3K27ac signal in the shared KLF4 peaks.