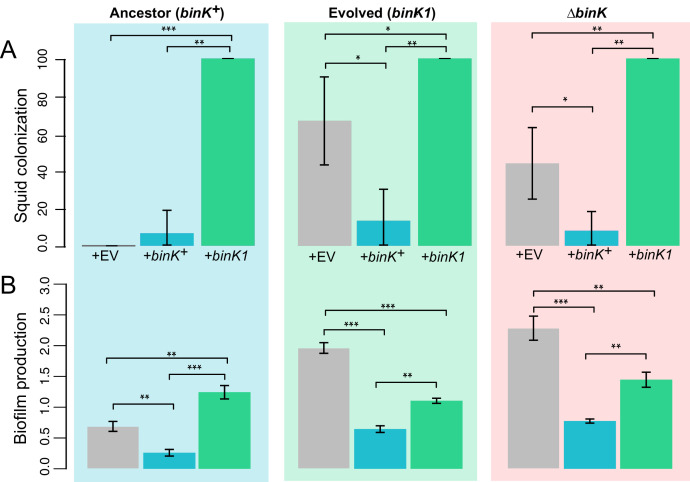
Figure 9. Effect of binK on squid colonization and biofilm production.
(A) Improvement in colonization by multi-copy in trans expression of the evolved binK1 allele and decreased colonization by expression of the ancestral binK+ allele. Colonization assessed by percentage of squid that are luminous after 24 hr. Error bars: 95% CI. N = 15–25. (B) Increased biofilm production resulting from in trans expression of the binK1 allele, and decreased biofilm production resulting from expression of the ancestral binK+. Comparisons of biofilm production in control-plasmids (pVSV105= EV) with that in multi-copy plasmids carrying binK suggest an inhibitory role for BinK in biofilm production, presumably alleviated by the dominance of the binK1 allele. Biofilm production was quantified by absorbance of crystal violet at A550. Background color depicts strain background in which multicopy plasmid effects were measured, mirroring those used throughout where blue is wild-type MJ11, green is the evolved binK1 variant and salmon is the ∆binK derivative. Error bars: 95% CI; non-overlap indicates significance. N = 7–8. Significant p-values (p<0.05) are indicated above each comparison. *p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.005.