Figure 3.
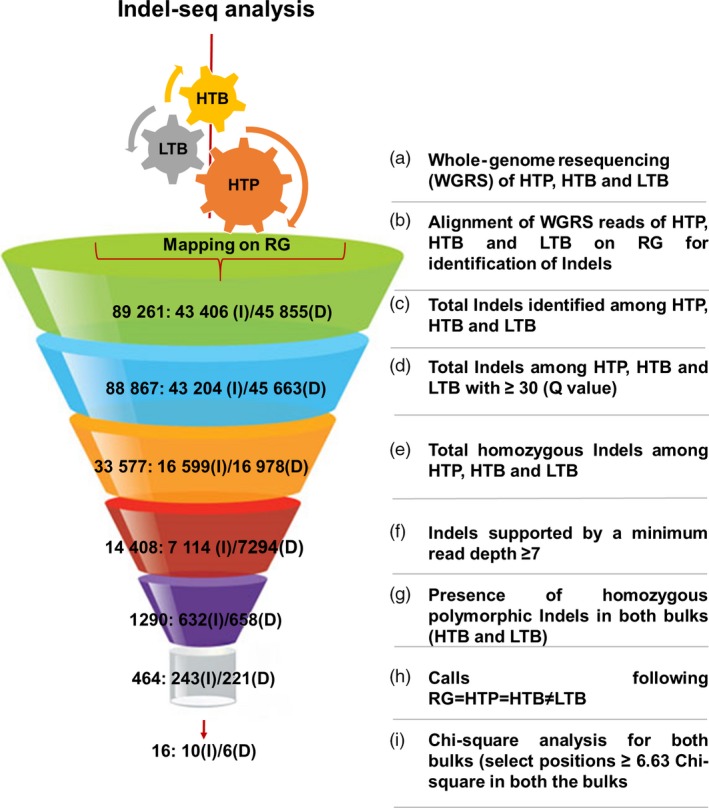
Flow diagram of Indel‐seq analysis for identification of candidate genes for FW and SMD resistance in pigeonpea. (a) Whole‐genome resequencing of the resistant parent (HTP), resistant bulk (HTB) and susceptible bulk (LTB) was performed with more than ≥10× genome coverage. (b) The generated raw reads of HTP, HTB and LTB were aligned with the reference genome (RG) for identification of genomewide Indels. The value presented in the funnel is the number of Indels identified/selected in each step, which is further classified as insertion (I) and deletion (D) (c) Total number of Indels identified after mapping of HTP, HTB and LTB on RG. (d) Further, only those Indels were selected, which possess ≥30 quality score. (e) Only homozygous Indels among HTP, HTB and LTB bulks were selected for further analysis (f) To remove false‐positive associations, only those Indels were selected which possesses reads ≥7 at both the bulk positions. (g) Homozygous polymorphic Indels were identified between both the bulks. (h) The classical concept of bulked segregant analysis (BSA) approach was implemented (RG = HTP = HTB ≠ LTB) for identification of putatively associated Indels (see text for the explanation). (i) Chi‐square test at 99% probability level was performed at each selected positions based on the presence of reads at selected Indel positions to select trait‐associated Indels.
