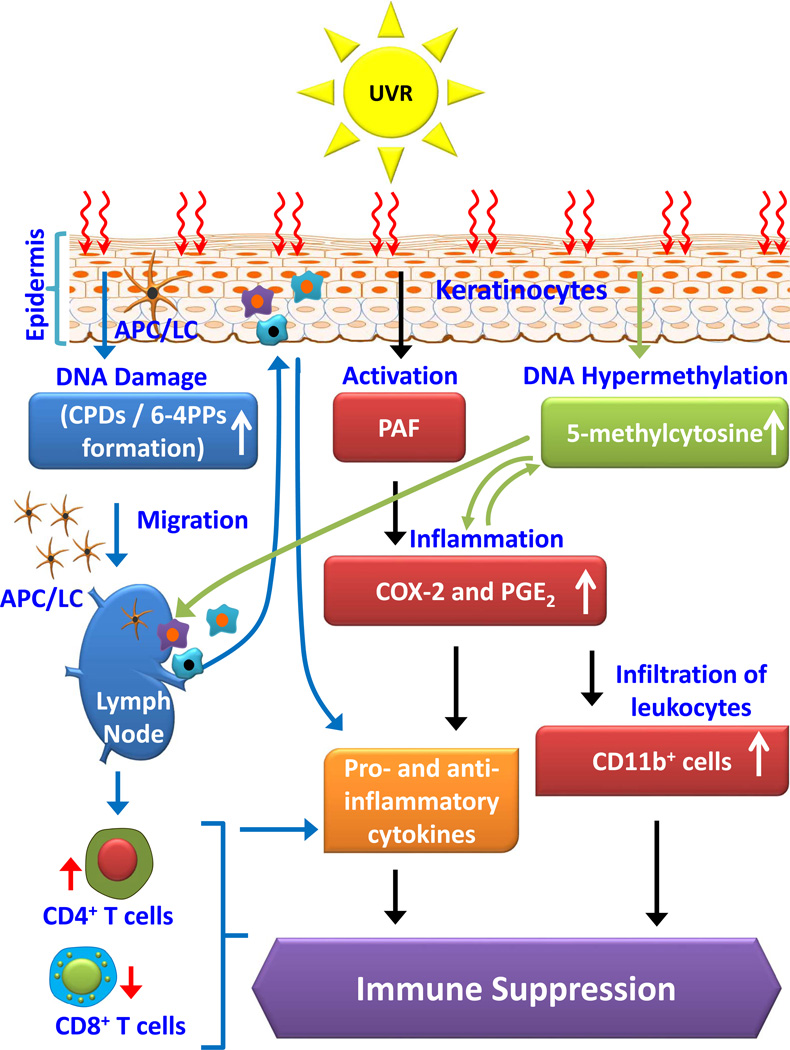
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram depicting dynamic crosstalk among UV radiation-induced inflammatory mediators, DNA damage, and epigenetic regulators in photo-immunosuppression. UVB induced photodamage initiates migration of antigen presenting cells from skin to regional lymph nodes, where they present antigen to T-cells in a way that is not normal due to photodamage of antigen presenting cells. UVB-induced inflammatory mediators and DNA damage affect epigenetic modifications (DNA hypermethylation) and together with infiltrating myeloid derived cells play crucial roles in suppression of immune system in UV radiation-exposed mice. UVR, ultraviolet radiation; CPDs, cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers; 6–4 PPs, 6–4 photoproducts; APCs, antigen presenting cells; PAF, Platelet activation factor; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; CD11b+ cells, activated macrophages and neutrophil cell population.