Figure 5.
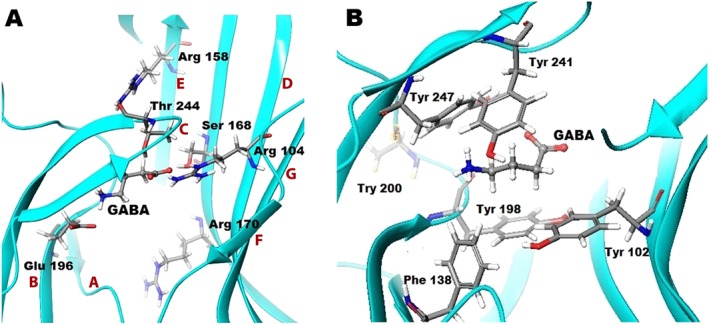
Molecular basis of GABA bound in the orthosteric binding site of GABA ρ1 homology model based on GluCl. (A) GABA bound GABA‐ρ1 homology model based on GluCl, showing loops A–G (labelled in red), and H‐bond interactions formed between GABA and Thr244 and Ser168, and salt bridges with Arg104 and Glu196. Arg158 and Arg170 are two important residues for protein stability either by forming interaction within the same subunit or between neighbouring subunits. (B) GABA and aromatic residues (Tyr102, Tyr198, Tyr241 and Tyr247) forming the aromatic box that stabilizes GABA in the binding site during the channel gating. The Phe138 residue may form important interactions as it has a benzene ring system that partially oriented to both the GABA binding site and the adjacent subunit.
