Figure 6.
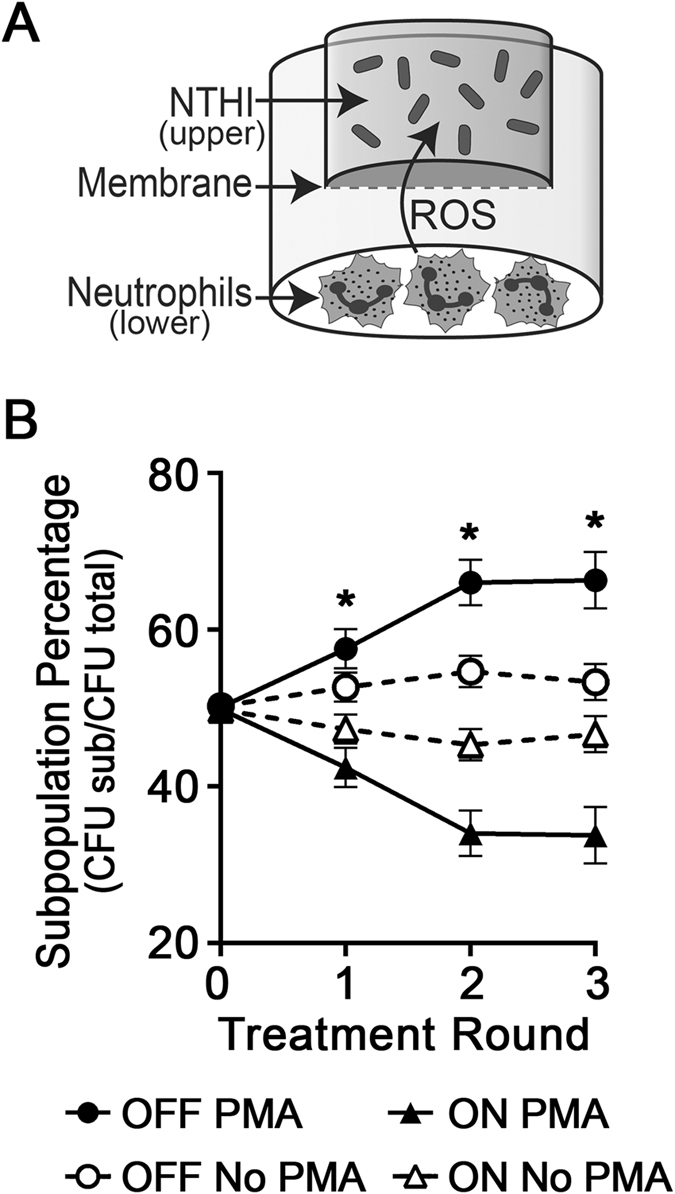
Exposure to ROS generated by human neutrophils selected for the modA2 locked OFF subpopulation. (A) NTHI and activated neutrophils were physically separated by a 0.4 µM pore membrane to prevent physical contact or phagocytosis, yet permit the diffusion of ROS. Neutrophils were seeded into the lower chamber of a Transwell system and activated with 50 nM PMA for 10 minutes. NTHI were then added to the upper chamber of a Transwell and incubated for 30 min to allow exposure to ROS. (B) A mixed culture that contained an equal number of modA2 locked ON:GFP and modA2 locked OFF:mCherry was subjected to multiple rounds of exposure to neutrophil-derived ROS. The increased sensitivity of modA2 locked ON to ROS resulted in an enrichment of the modA2 locked OFF subpopulation. Selection was apparent after the first round of exposure to ROS. The population percentages, modA2 locked ON compared to modA2 locked OFF, were significantly different after the first round, *P < 0.005, unpaired t-test. This difference remained significant after each subsequent round of exposure to ROS, *P < 0.005, multiple t-tests. These data suggest that ROS due to infiltrating immune cells will contribute to selection for the modA2 OFF status.
