Figure 5.
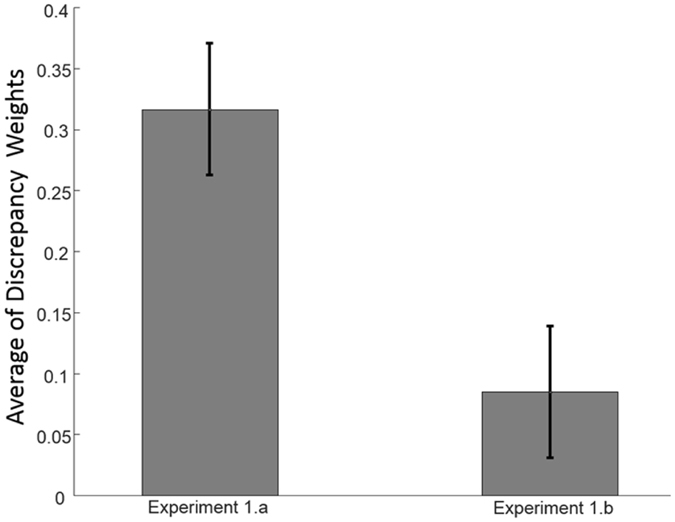
Discrepancy Weights. The discrepancy weights depend on the relative reliability of the cues across the different reliability conditions. Discrepancy weights are inversely correlated to the probability of the common cause P C. Thus, the lower discrepancy weight in the experiment 1.b indicates a higher probability of an assumed common cause, which is consistent with the observed behavior in that experiment. In contrast, the higher discrepancy weight in the experiment 1.a points to a lower common cause probability that explains the selection strategy in experiment 1.a.
