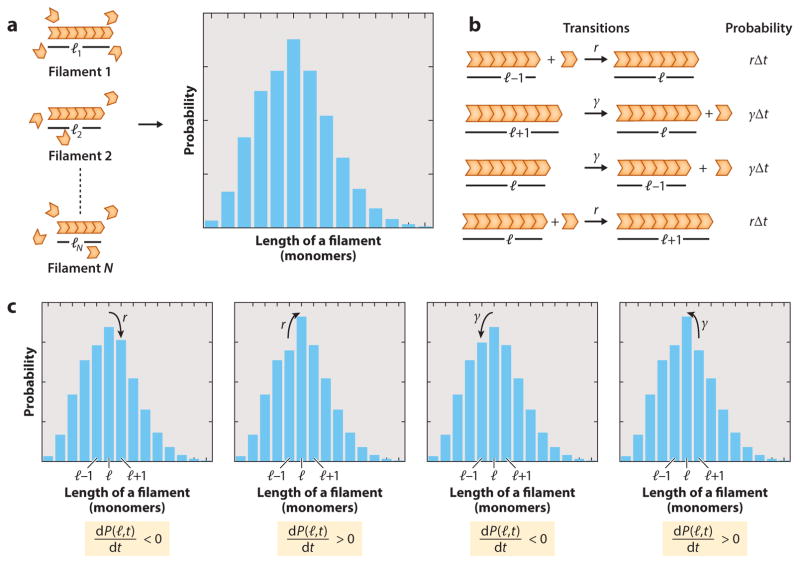
Figure 3.
Master equation for dynamics of filament assembly. (a) P(l, t) is the frequency of occurrence of filaments of length l in an ensemble of dynamical filaments at time t. (b) List of all transitions that lead to a change in the probability of a filament having a length l. A filament can either grow starting as a filament of length l − 1 by adding a subunit with a rate r or shrink by starting as a filament of length l + 1 by losing a subunit with a rate. These transitions will increase P(l, t) by rΔt or γ Δt, respectively. Alternatively, a filament of length l can either shorten to a filament of length l − 1 with a rate or add a subunit and become a filament with length l + 1 with a rate r. These transitions will decrease P(l, t) by γ Δt or rΔt, respectively. (c) Changes in the probability distribution due to different molecular processes, described in panel b.