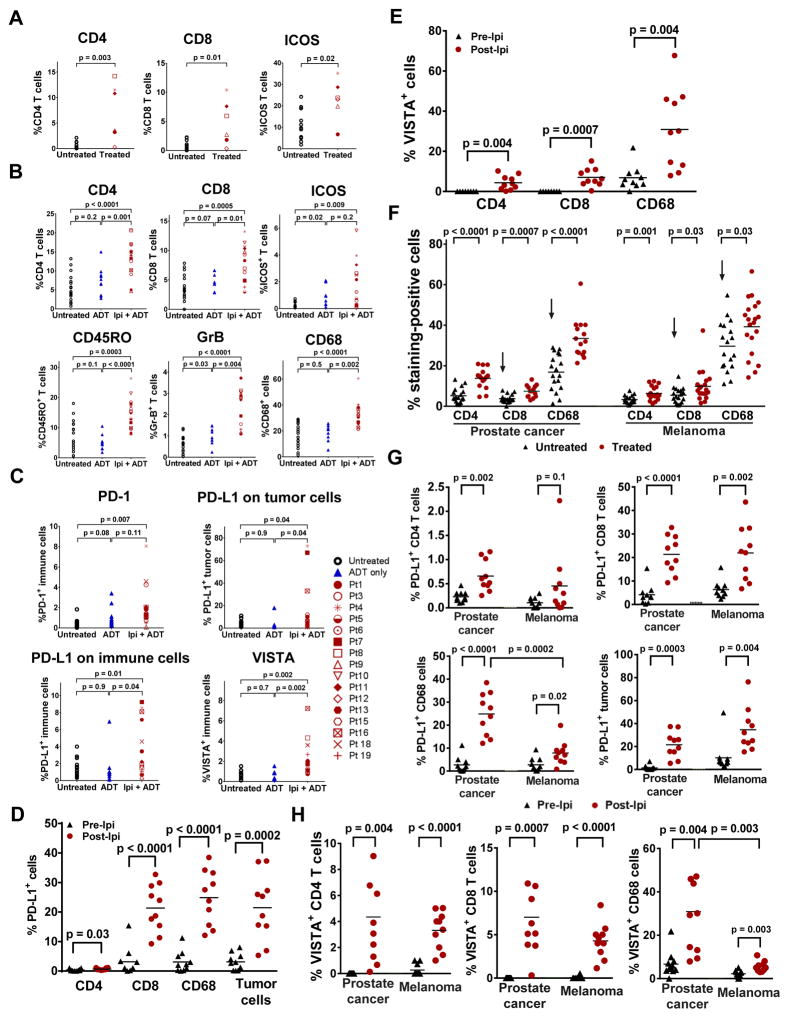
Figure 1. Treatment with ipilimumab increases immune cell infiltration, as well as expression of PD-L1 and VISTA in prostate tumors.
(a) Frequency of CD4, CD8 and ICOS+ T cells in untreated (N=11) and treated (N=6) tumors. (b) IHC analyses of CD4, CD8, ICOS+, CD45RO+, and GrB+ T cells, as well as CD68+ macrophages. (c) IHC of PD-L1, PD-1, and VISTA in tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating immune cells, with b-c comprised of tumors from 3 different cohorts of stage-matched patients: untreated (N=18), ADT-treated (N=10), and ipilimumab + ADT (N=16). Asterisk indicates patients received high dose steroids with surgery delay. (d) Frequency of PD-L1 expression on CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, CD68+ macrophages, and tumor cells. (e) Frequency of VISTA expression on CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, and CD68+ macrophages, with d-e comprised of matched pre-treatment (N=10) and post-treatment tumors (N=10). (f) IHC staining of CD4 and CD8 T cells, and CD68+ macrophages in stage-matched untreated (N=18) and ipilimumab + ADT-treated (N=15) prostate tumors as compared to stage-matched untreated (N=18) and ipilimumab-treated (N=20) metastatic melanomas. Arrows indicate significant difference of CD8 T cells and CD68+ macrophages between untreated prostate tumors and untreated melanomas. (g) Frequency of PD-L1 expression on CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, and CD68+ macrophages. (h) Frequency of VISTA expression on CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, and CD68+ macrophages, with g-h comprised of matched pre-treatment (N=10) and post-treatment prostate tumors (N=10) as compared to matched pre-treatment (N=10) and post-treatment melanomas (N=10).