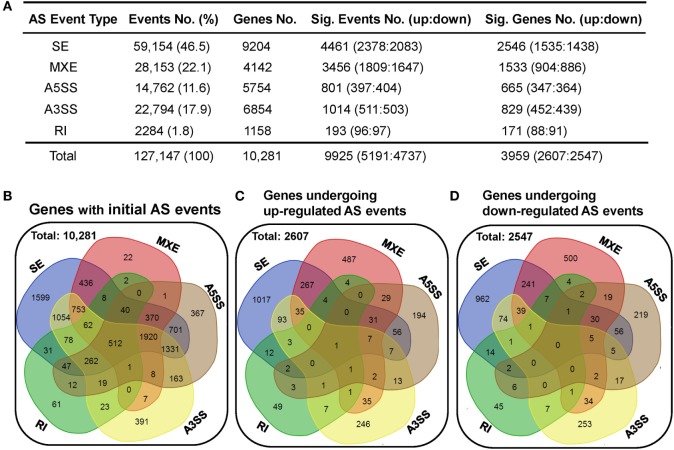
Figure 5.
dCD4 T cells undergo a comparable number of upregulated and downregulated AS events. (A) Summary of the numbers of five types of AS events, differentially expressed events (with upregulated and downregulated events) and the genes they belong to. Column 1 shows the five most common types of AS events that were investigated. Columns 2 and 3 show the initial number of AS events found in the combined samples of pCD4 and dCD4 T cells with their frequency among total events (column 2), as well as the number of genes these events belong to (column 3). Columns 4 and 5 show the number of differentially expressed events (FDR < 0.05 with |ΔΨ| > 0.05 between samples) with upregulated (FDR < 0.05 with ΔΨ > 0.05) and downregulated (FDR < 0.05 with ΔΨ < −0.05) AS events in dCD4 T cells versus their autologous pCD4 T counterparts (column 4), as well as the number of genes that these significant events belong to (column 5). (B) Venn diagram of genes showing the initial SE, MXE, A5SS, A3SS, and RI in the combined samples (pCD4 and dCD4 T cells). (C,D) Venn diagram of genes showing upregulated (C) or down-regulated (D) SE, MXE, A5SS, A3SS, and RI events in dCD4 T cells with respect to pCD4 T cells. AS, alternative splicing; SE, skipped exon; MXE, mutually exclusion exons; A5SS, alternative 5′ splice site; A3SS, alternative 3′ splice site; RI, retained intron; %, percentage; No., Number; Sig., Significant; up, upregulated; down, downregulated; FDR, false discovery rate.