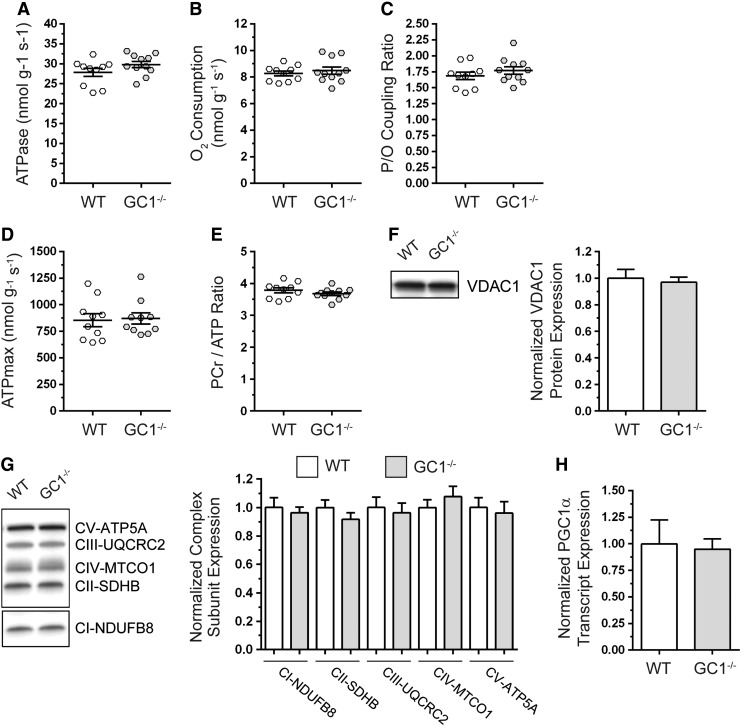
FIG. 7.
GC1 is dispensable for resting skeletal muscle mitochondrial ATP synthesis and content. Mitochondrial ATP generation and oxygen consumption in hind limb skeletal muscles of anesthetized WT and GC1−/− mice were simultaneously measured by in vivo 31P magnetic resonance and optical spectroscopy. (A) Mitochondrial ATP synthesis, which is directly proportional to ATPase activity. (B) Mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate. (C) Mitochondrial ATP synthesis efficiency as determined from the P/O coupling ratio, where P (ATP generation) is divided by oxygen consumption rate (O). (D) Mitochondrial ATP synthesis capacity (ATPmax). (E) Phosphocreatine-to-ATP ratio. For (A–E), n = 9–10 for WT and 10–11 for GC1−/− groups, respectively. (F) Representative Western blot and densitometric quantitation of mitochondrial marker VDAC1 expression in tibialis anterior muscles. n = 5 for WT and GC1−/− groups. (G) Representative Western blot and densitometric quantitation of mitochondrial respiratory complex subunit expression in tibialis anterior muscles. (H) Quantitation of PGC1α transcript expression by qPCR. For (G, H), n = 6 for WT and GC1−/− groups.