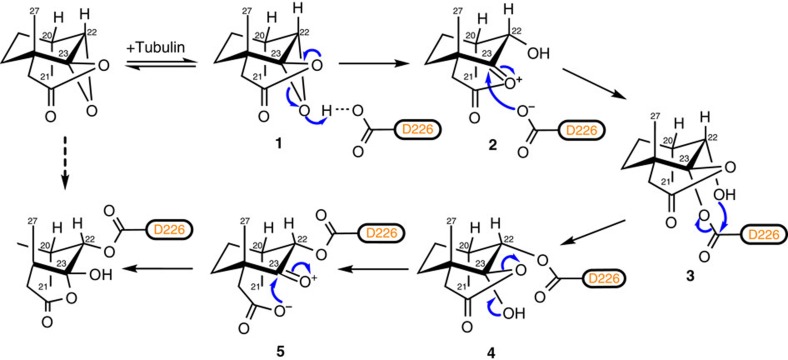
Figure 3. Possible reaction mechanisms of the ester bond between taccalonolide AJ and β-tubulin D226.
When AJ binds to the taxane site, the epoxy ring between C22 and C23 approximates the carboxyl group of βD226 and is activated by protonation; then, C23 is attacked by the carboxylate of D226 resulting in the formation of the oxirane ring-opening hydroxyl intermediate 3, followed by an interesterification to form intermediate 4. The five-membered ring of intermediate 4 has two adjacent carbons on the six-membered ring in trans position, in which the ring strain is relatively large, thus driving to proceed another interesterification to form the complex 5, as observed in the crystal structure.