Figure 1. Difficulties associated with studying lncRNAs.
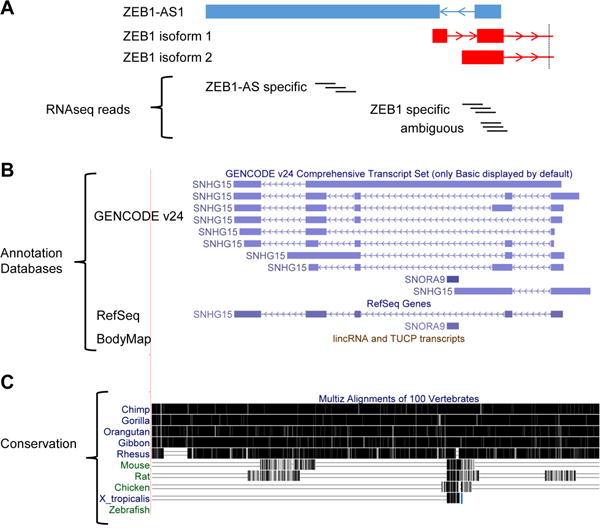
(A) Unstranded RNAseq reads can be ambiguous when mapping to antisense lncRNAs. (Top) Annotations of lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 (blue) and two ZEB1 PCG isoforms (red; cropped for simplicity). Arrows indicate the direction of transcription. (Bottom) RNAseq reads are accurately assigned when they align to specific exons of the antisense pair, but are ambiguous when they map to the shared exons. (B) Annotations between databases vary. Annotation of SNHG15 from three commonly used databases— GENCODE, RefSeq, and BodyMap—are shown. BodyMap does not include an annotation for SNHG15. (C) LncRNAs are not highly conserved. The conservation of SNHG15 is shown with black bars representing sequence conservation between different species. Note that SNHG15 is only conserved among primates.
