Fig. 1.
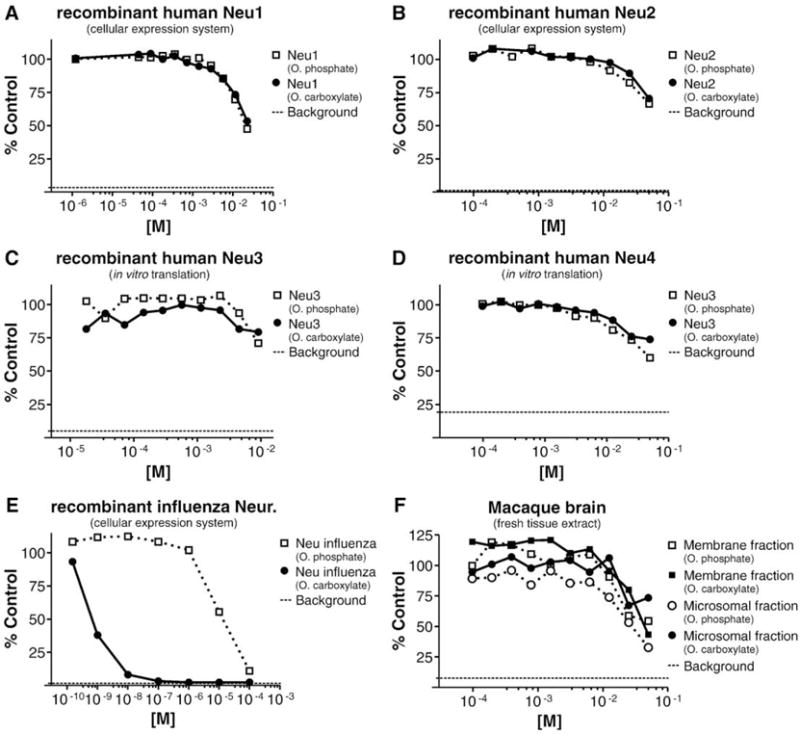
Assessment of oseltamivir phosphate and oseltamivir carboxylate for inhibitory activity against recombinant human NAs Neu1–4, recombinant influenza virus NA, and brain extract NA activity. Human (A–D) and influenza (E; strain A/Beijing/39/1975 H3N2) NAs were expressed by in vitro translation or by transient transfection in CHO cells. Brain extracts (F) were prepared from fresh Macaca fascicularis brain tissue. NA assays as described by Potier et al. (1979) with modifications (see Supplemental methods for assay details). For the transient transfection, the separation between the NA activity present in lysates of CHO cells either mock transfected or transfected with human or influenza NAs was ~ 3-fold for Neu1, ~ 10-fold for Neu2, and > 10-fold for influenza NA. Background: Signal obtained with mock in vitro translation (C and E) or with the reaction mixture lacking cell or tissue lysates (A, B, E, and F).‘% control’: Calculated as‘% control’ = 100 × RFU (test sample) /RFU (reference sample), with RFU = relative fluorescent unit; test sample = mixture of NA activity, substrate, and oseltamivir phosphate/oseltamivir carboxylate; reference sample = mixture of NA activity and substrate without oseltamivir phosphate or oseltamivir carboxylate.
