Figure 6. Cryo EM structure of PqiB reveals architecture of a periplasmic bridge.
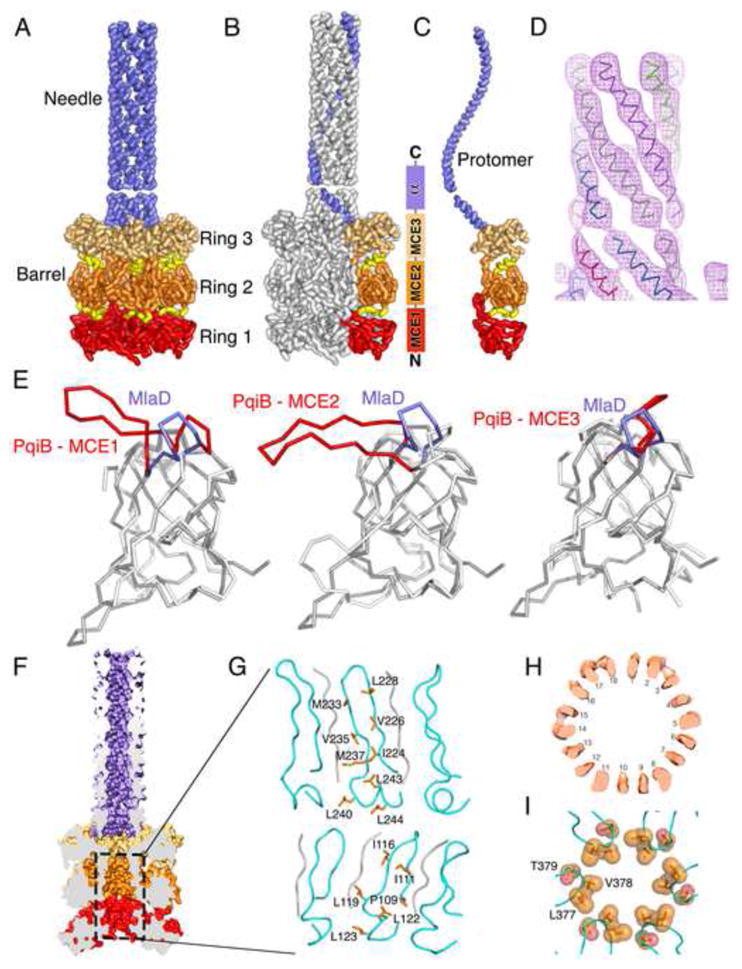
(A) Side view of PqiB, with the IM at bottom and the OM at top. The MCE1, MCE2, and MCE3 rings of the barrel (red, orange, and tan, respectively), and inter-ring connectors (yellow) are shown. The C-terminal “needle” is colored lilac.
(B and C) Similar to (A), but with single subunit colored in the complex (B), and in isolation (C).
(D) Helical density for the first half of the needle, proximal to the barrel.
(E) Superposition of the MlaD MCE domain on PqiB’s MCE1, MCE2, and MCE3 domains. The β5-β6 loop of MlaD is in lilac and the homologous PqiB loops in red.
(F) Surface representation of PqiB, cut in half vertically to reveal a long tunnel running from the tip of the needle to the bottom of the barrel.
(G) Ribbon representation of the boxed region in (F), showing the interior/lumenal surface of the barrel’s pore. The β5-β6 loops are depicted in cyan, with additional polyalanine strands in gray. The side chains facing the pore lumen are shown as orange sticks and labelled.
(H) Horizontal slice through the upper 18-stranded β-barrel motif of PqiB barrel, revealing 18 tubes of density.
(I) Residues from the β5-β6 loop of PqiB’s MCE3 domain form a constriction between the barrel and the needle. Top view (from OM towards IM), with β5-β6 loops in cyan and key residues as labeled orange spheres.
