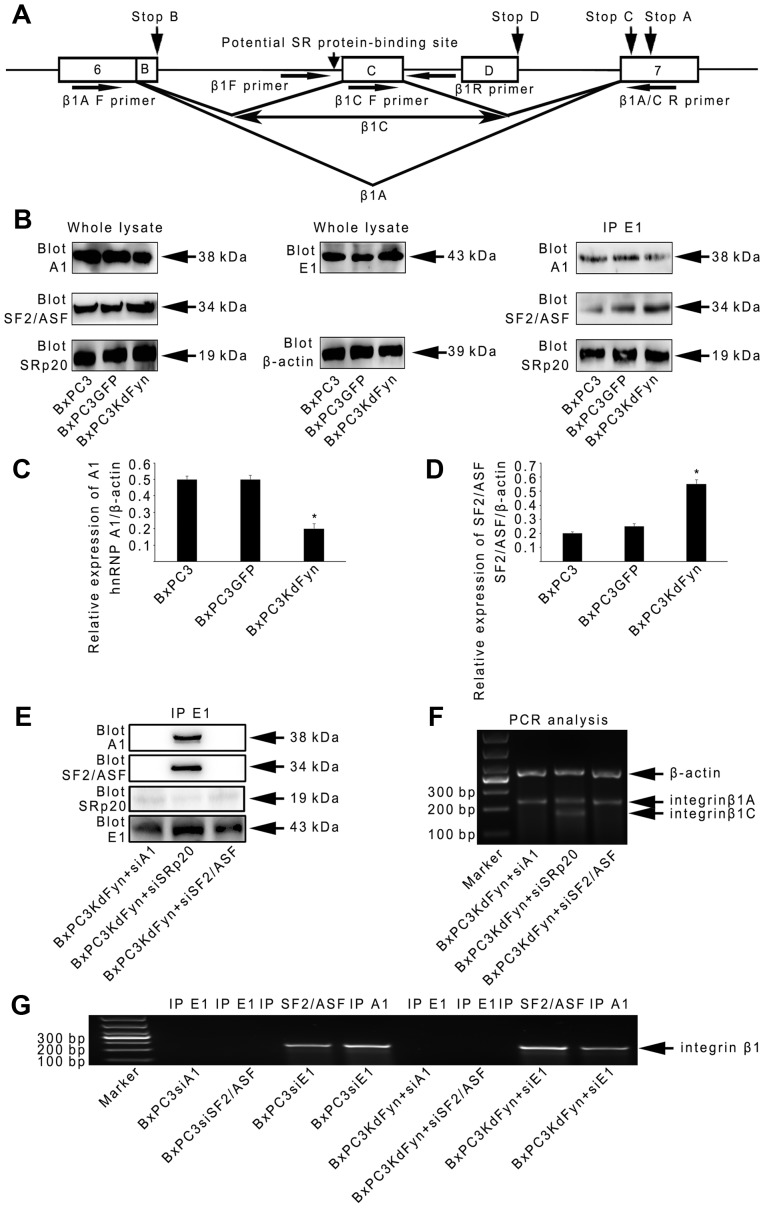
Figure 4.
hnRNP E1 spliceosome regulates integrin β1 splicing by hnRNP A1 and SF2/ASF. (A) Schematic representation of the genomic sequence of integrin β1. Exon sequences are shown as boxes and introns as solid lines. The splicing pattern used to generate β1A and C transcripts are depicted, and the potential SR protein-binding site is indicated with a vertical arrow. The positions of the stop codons for the various splice variants are also indicated by arrows. The horizontal arrows indicate the primers used in PCR experiments (Table I). (B–D) Western blot analysis and co-immunoprecipitation were used to analyze the expression levels and abundance of hnRNP E1-specific spliceosome components among BxPC3, BxPC3GFP and BxPC3KdFyn cells. β-actin blotting was used as a loading control. (E and F) Co-immunoprecipitation and splicing analysis were used to explore the functions of hnRNP A1 and SF2/ASF on the construction of the hnRNP E1 spliceosome complex and the splicing of integrin β1. (G) RNA immunoprecipitation showed that hnRNP A1 and SF2/ASF, but not hnRNP E1, were directly bound to the pre-mRNA of integrin β1. *P<0.05. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from ≥3 independent experiments.