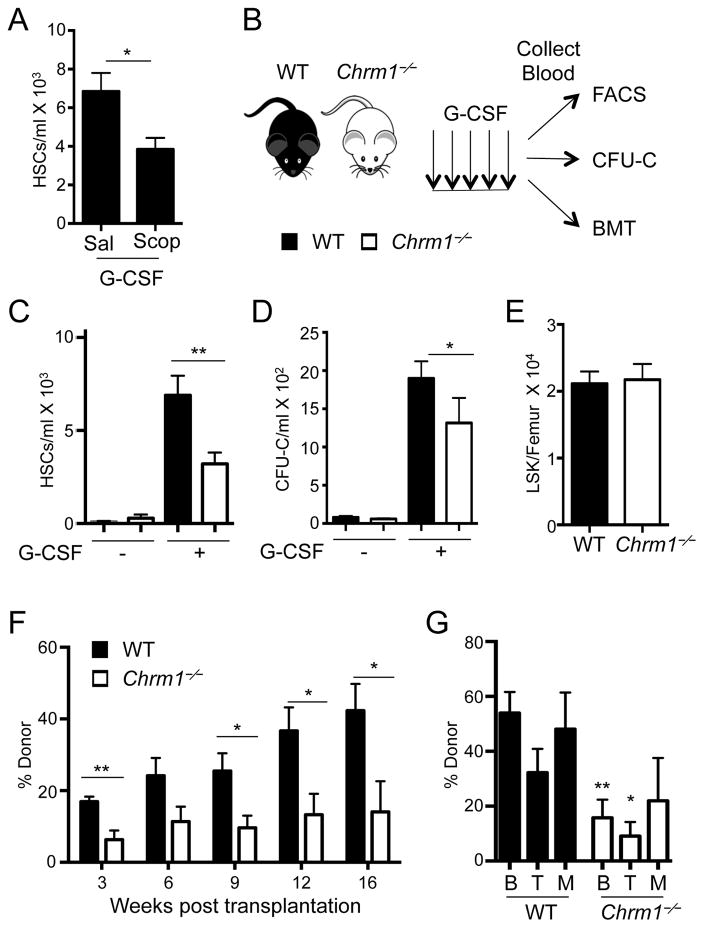
Figure 1. G-CSF-induced HSC mobilization requires signals from the muscarinic receptor type-1 (Chrm1).
(A) HSCs/mL following G-CSF mobilization in wild-type mice treated with saline or Scopolamine hydrobromide (Scop 1mg/kg; n = 5–8). HSCs defined as Lineage− Sca1+ cKit+ Flt3−.
(B) Schematic of G-CSF-induced mobilization and analyses. Wild-type mice are denoted by black bars and Chrm1−/− mice by white bars.
(C) HSCs/ml of peripheral blood (Lineage− Sca1+ cKit+ Flt3−; n = 12–16)
(D) Colony-forming units/ml of peripheral blood determined in vitro (CFU-C; n = 6–13).
(E) Lineage− Sca1+ cKit+ (LSK) cells/femur at steady state (n = 9).
(F) Reconstitution after competitive BM transplantation of mobilized blood into irradiated hosts
(G) Tri-lineage engraftment of donor cells 16 weeks post transplantation: B220+ cells (B) CD4/CD8+ cells (T) and Mac1+ cells (M; n= 6–7).
* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 determined by Student’s t test. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S1.