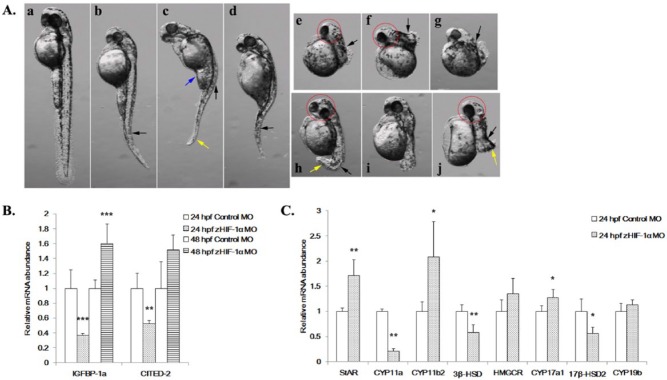
Figure 3.
Effects of zHIF-1α knockdown on zebrafish embryonic development and the expression of hypoxia markers and steroidogenic genes under normoxia. (A) Morphological abnormalities of the zHIF-1α knockdown embryos at 48 hpf under normoxia. The effect of zHIF-1α knockdown on steroidogenic gene expression was examined by microinjecting zHIF-1α MOs into 1- to 2-cell stage zebrafish embryos and maintained under either normoxia or hypoxia. Zebrafish embryos microinjected with a standard control MO were used as controls. All morphants were imaged at the left lateral view. a, Control: embryo injected with control MO; b-j, embryos microinjected with zHIF-1α MO; b, c, and d, morphants with decreased body length, bended notochords (black arrows), and distorted abdomens (blue arrows); e-j, morphants with bended notochords, small head circles (red circles), and short curved tail (yellow arrows). (B) Effects of zHIF-1α knockdown on IGFBP-1a and CITED-2 expression under normoxia. (C) Effects of zHIF-1α knockdown on steroidogenic gene expression under normoxia. Gene expression was quantified by real-time PCR and normalized against β-actin mRNA. Data are presented as the mean relative fold change ± SD with respect to the gene expression level in the control (its expression level was arbitrarily set to 1) for each experiment. Expression levels significantly different from the control are indicated by asterisks (t test, n ⩾ 4, *P ⩽ .05, **P ⩽ .01, ***P ⩽ .001). mRNA indicates messenger RNA; MO, morpholino oligonucleotide.