Abstract
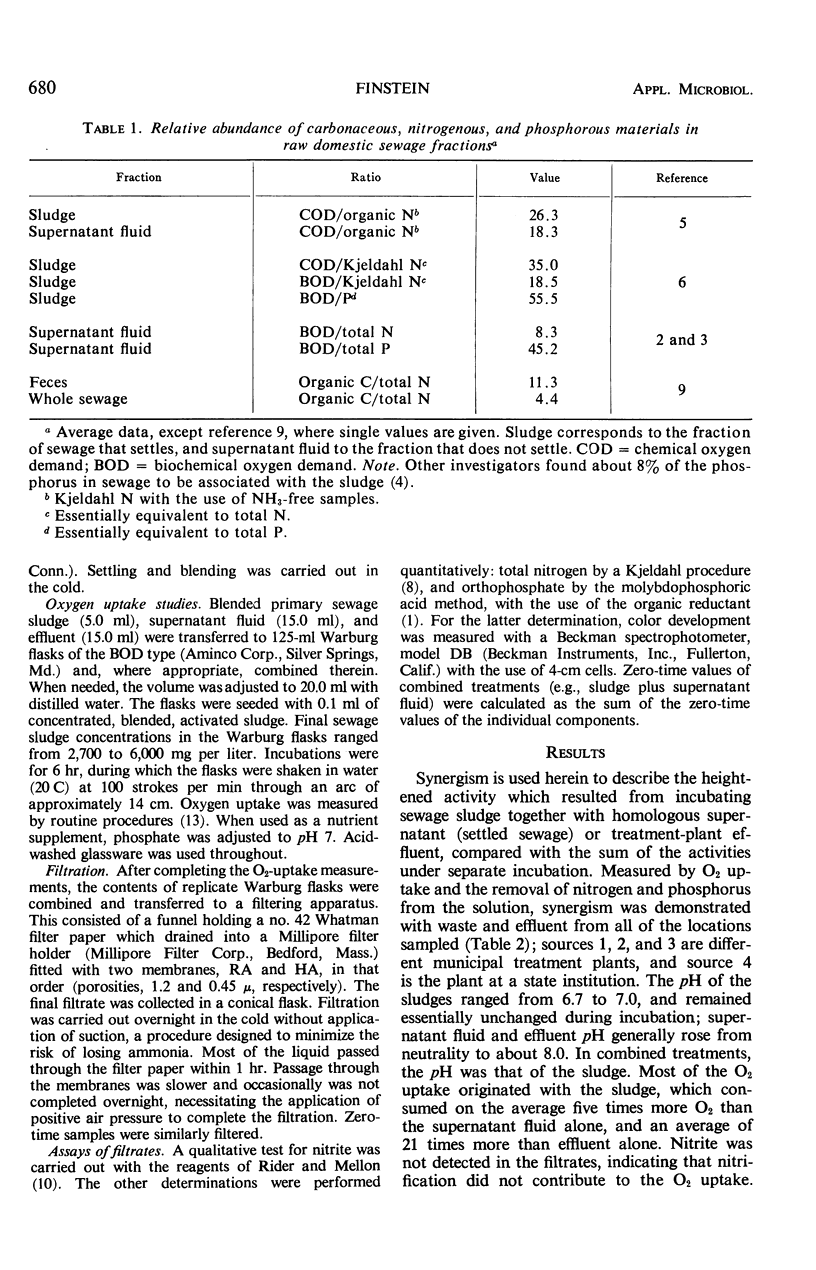
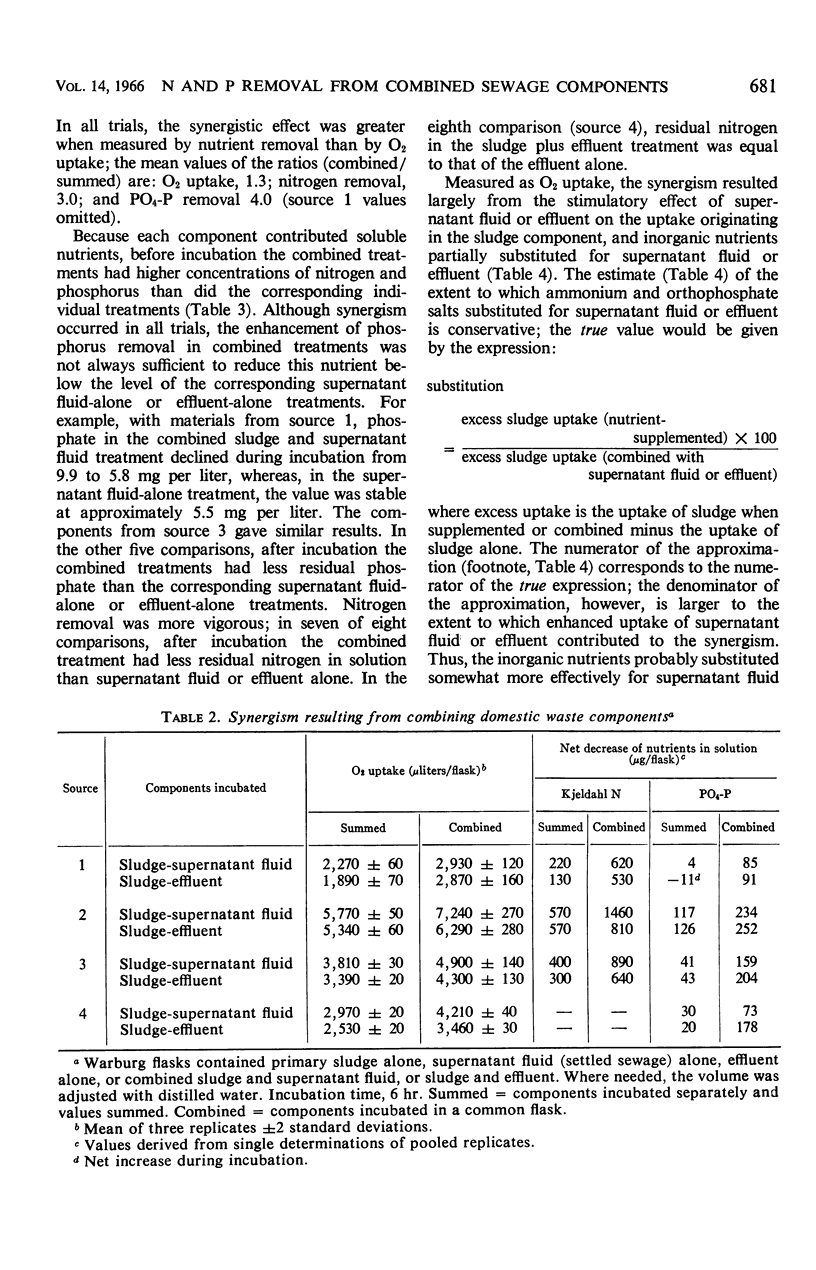
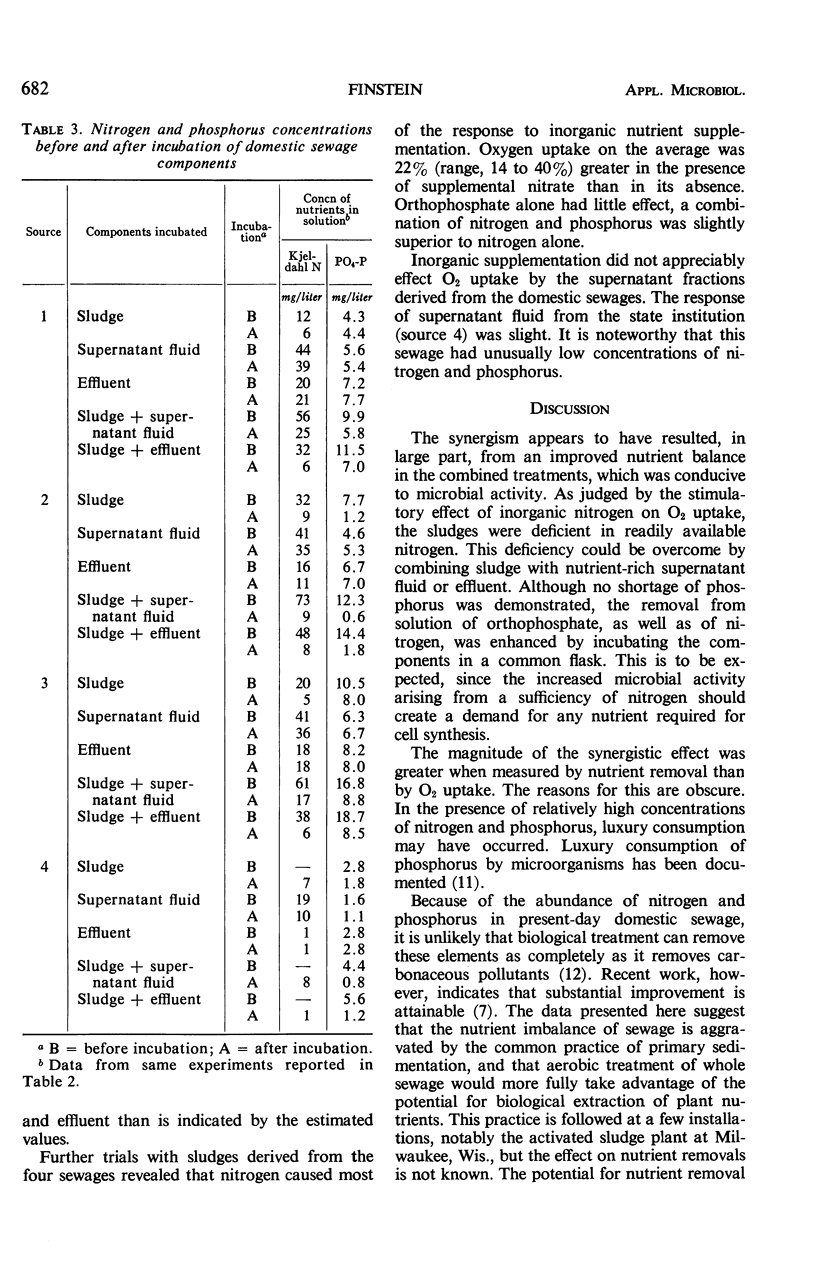
When primary domestic sewage sludge was combined with settled sewage or secondary-treatment plant effluent, synergism resulted. The activity (measured by oxygen uptake, and the removal of Kjeldahl nitrogen and orthophosphate from solution) which resulted from incubating sludge together with settled sewage exceeded the sum of the activities when these components were incubated separately. A similar synergistic effect occurred with sludge and effluent. The sewage sludges were deficient in readily available nitrogen, but no shortage of phosphorus was demonstrated. The addition of ammonium and orthophosphate salts to sludge, in concentrations equivalent to those found in settled sewage and effluent, stimulated sludge oxygen uptake at least 80% as much as settled sewage or effluent. It is suggested that the synergism reflects increased microbial activity resulting from widened carbon-nitrogen and carbon-phosphorus ratios achieved by combining sludge with nutrient-rich settled sewage or effluent.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- IRGENS R. L., HALVORSON H. O. REMOVAL OF PLANT NUTRIENTS BY MEANS OF AEROBIC STABILIZATION OF SLUDGE. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:373–386. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.373-386.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH I. W., WILKINSON J. F., DUGUID J. P. Volutin production in Aerobacter aerogenes due to nutrient imbalance. J Bacteriol. 1954 Oct;68(4):450–463. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.4.450-463.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


