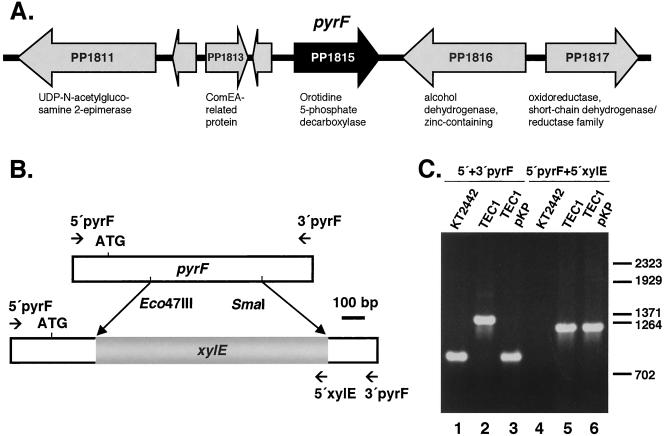
FIG. 1.
Generation of ΔpyrF P. putida TEC1. (A) Schematic diagram of the P. putida pyrF gene (ORF PP1815) chromosomal context. The locus name of each ORF with assigned or predicted function is shown; hypothetical ORFs are unmarked. (B) Schematic diagram of the P. putida pyrF gene and of the ΔpyrF in P. putida TEC1. The xylE gene was cloned in the Eco47III and SmaI sites of pyrF. Primers are shown as arrows, indicating primer combinations used to amplify the pyrF and xylE sequences. (C) PCR analysis of wild-type and ΔpyrF strains. Lanes 1 to 3: primers annealing to the pyrF promoter and to the 3′ end of the gene were used to amplify the pyrF gene of P. putida KT2442, of the ΔpyrF strain P. putida TEC1, and of TEC1 with the pyrF-containing pKP plasmid. Lanes 4 to 6: the chromosomal copy of ΔpyrF in P. putida TEC1 carrying pKP was amplified with primers annealing at the 5′ end of pyrF and xylE.