Figure 1.
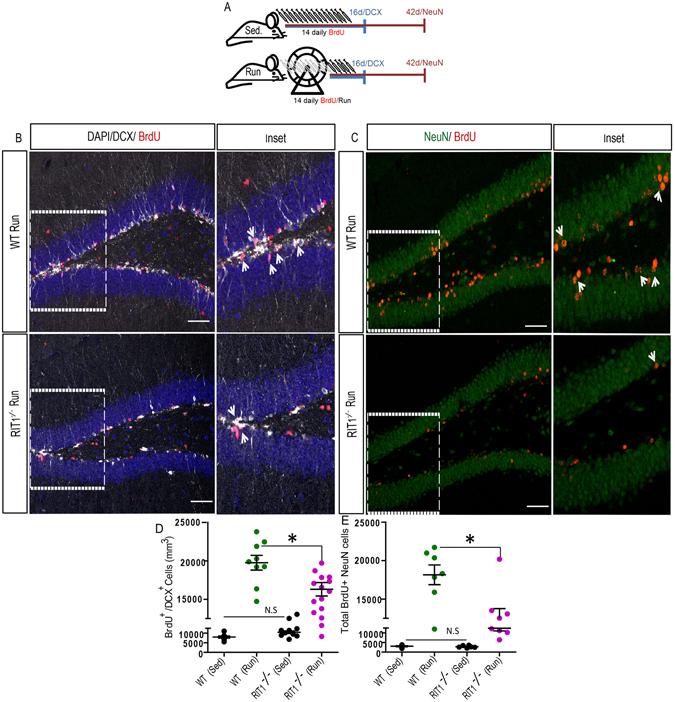
Adult neurogenesis in RIT1 −/− and WT littermates housed under running conditions. (A) Schematic of experimental design (see methods for details). WT and RIT1 −/− mice were injected daily with BrdU (50 mg/kg, i.p) for 14 days while housed in either sedentary or running cages and either analyzed for newborn neuroblasts (DCX+/BrdU+) (day 16) or the generation of mature neurons (NeuN+/BrdU+) (day 42). Representative coronal hippocampal sections from the dentate gyrus of (B) 16d mice immunostained for DCX (white, pseudocolor), BrdU (red, white arrowheads) and DAPI, or (C) 42d mice co-immunostained with NeuN (green) and BrdU (red; white arrowheads). The inserts are at higher magnification. The arrow heads indicate either newborn neuroblasts (B) or mature neurons (C). Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Quantitative analysis of newborn immature hippocampal neurons (BrdU+/DCX+) following 16 days of running or sedentary housing (*p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA). (E) Quantitative analysis of BrdU+ mature neurons (NeuN+) at day 42 (*p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA). The results are presented as mean ± SEM (WT, n = 17; RIT1 −/−, n = 23).
