Figure 1.
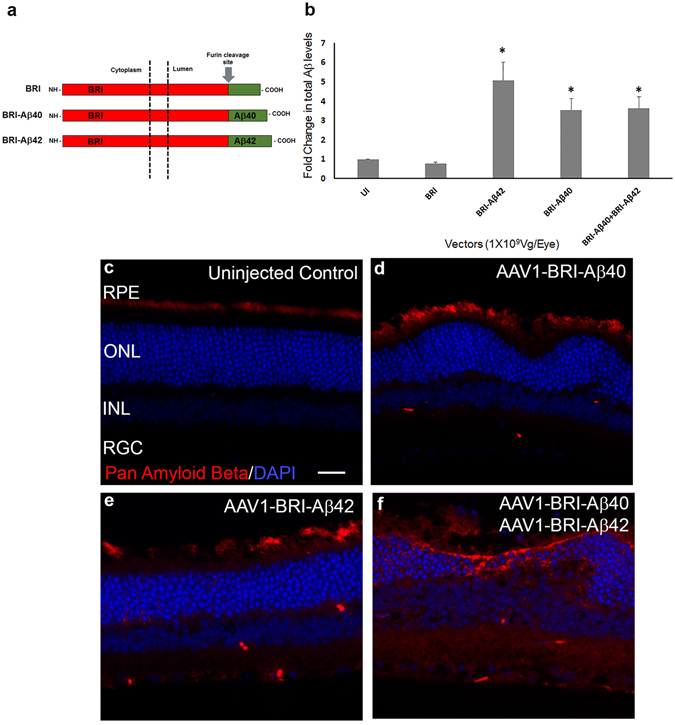
ELISA analysis and immunostaining to evaluate the expression of Aβ 8 weeks after sub-retinal injection of AAV1 vectors. (a) Schematic of the BRI-Aβ fusion constructs used to generate AAV1 vectors (modified from41) Control vector contains BRI protein that has been truncated at the protease site. (b) ELISA analysis for total Aβ showing a significant increase in the level of expression in the single vector injected and combination vector injected retinas when compared to age-matched un-injected (UI) and control vector AAV1-BRI injected retinas. An equal increase in level of Aβ expression in retinas receiving sub-retinal injection of AAV1-BRI-Aβ40, AAV1-BRI-Aβ42 and the combination of the two vectors AAV1-BRI-Aβ40+AAV1-BRI-Aβ42 is observed. n = 4/group, bars in this graph represent mean +/− SEM, Student’s t-test was performed to measure significance between the vector injected groups and the un-injected control group. *p < 0.05 is considered significant. (c–f) Aβ immunostaining of retinal sections from each experimental group shows that human Aβ is expressed only in eyes that received sub-retinal injection of AAV1-BRI-Aβ40, AAV1-BRI-Aβ42 and AAV1-BRI-Aβ40+AAV1-BRI-Aβ42. Scale Bar = 20 μm. RPE: retinal pigment epithelium; ONL: outer nuclear layer; INL: inner nuclear layer; IPL: inner plexiform layer; RGC: retinal ganglion cells.
