FIGURE 1.
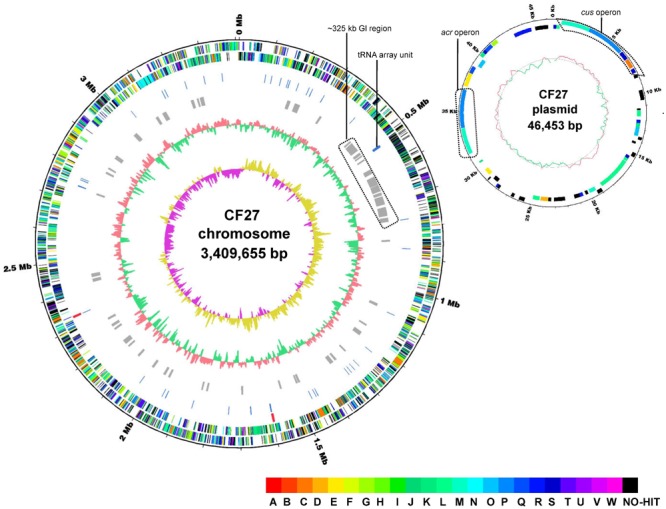
Circular representation of the At. ferrivorans CF27 chromosome (A) and plasmid (B). The closed loop chromosome (A) provides the following information (from outside to inside): (1) position (in megabases); (2) forward strand CDSs; (3) reverse strand CDSs (colors indicating the assigned COG classes); (4) rRNAs (red); (5) tRNAs (blue); (6) predicted genomic islands; (7) G + C content (red indicates higher G + C compared with the chromosome average G + C content and green indicates lower G + C content); (8) GC skew (purple indicates positive values and yellow, negative values). The tRNA array unit as well as the ∼325 Kbp genomic island (GI) region are shown. The closed loop plasmid (B) shows (from outside to inside): (1) position (in megabases); (2) forward strand CDSs; (3) reverse strand CDSs (colors indicating the assigned COG classes); (4), G + C content (red indicates higher G + C compared with the plasmid average G + C content and green indicates lower G + C content). Multi-drug efflux system (acr) and copper resistance (cus) operons are shown. COG categories are shown in different colors (see the COG color legend) and are associated with the corresponding capital letters: A, RNA processing and modification; B, chromatin structure and dynamics; C, energy production and conversion; D, cell cycle control, cell division, and chromosome partitioning; E, amino acid transport and metabolism; F, nucleotide transport and metabolism; G, carbohydrate transport and metabolism; H, coenzyme transport and metabolism; I, lipid transport and metabolism; J, translation, ribosomal structure, and biogenesis; K, transcription; L, replication, recombination, and repair; M, cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; N, cell motility; O, posttranslational modification; protein turnover, chaperones; P, inorganic ion transport and metabolism; Q, secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism; R, general function prediction only; S, function unknown; T, signal transduction mechanisms; U, intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; V, defense mechanisms; W, extracellular structures; NO-HIT, proteins not belonging to COG categories.
