Fig. 1.
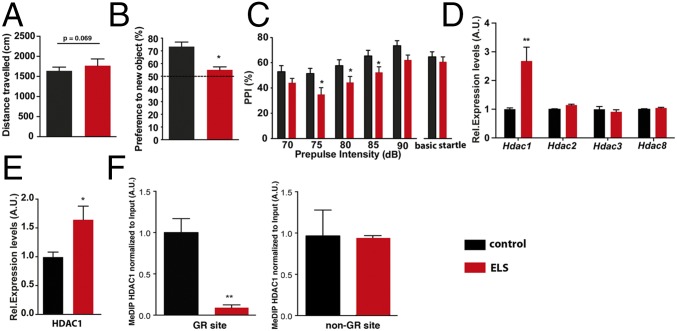
Expression of HDAC1 is elevated in mice exposed to ELS. (A) Mice subjected to ELS show normal explorative behavior (n = 15 per group), although there was a trend for locomotor hyperactivity (P = 0.069, unpaired Student’s t test). (B) Short-term memory analyzed via the novel object recognition paradigm revealed impairment in ELS-exposed mice (*P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test). (C) PPI was impaired in ELS mice. Two-way ANOVA of repeated measurements showed a significant effect of ELS [F(4,41) = 5.341, *P = 0.0259] and a significant effect of prepulse intensity [F(4,164) = 2.123]. A Bonferroni post hoc test revealed significant impaired PPI at 75 dB (P = 0.0089), 80 dB (P = 0.0356), and 85 dB (P = 0.0389). (D) Mice were subjected to ELS, and the prefrontal cortex (PFC) was isolated at PND120. qPCR analysis showed that Hdac1 mRNA is up-regulated in ELS-exposed mice compared with the control group (n = 6 per group; **P < 0.01, unpaired Student’s t test). Other class I HDACs were not affected. A.U., arbitrary units; Rel., relative. (E) Immunoblot analysis (n = 5 per group) confirmed elevated HDAC1 protein levels in the PFC from ELS-exposed mice. Tissue was isolated at PND120 (*P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test). (F, Left) MeDIP followed by qPCR shows that ELS leads to reduced DNAme of the Hdac1 gene at the GR-binding site (**P < 0.01, unpaired Student’s t test; n = 5 per group). Tissue was isolated at PND120. (F, Right) MeDIP followed by qPCR revealed no difference when a non-GR DNAme site within the Hdac1 gene was tested. Error bars indicate SEM.