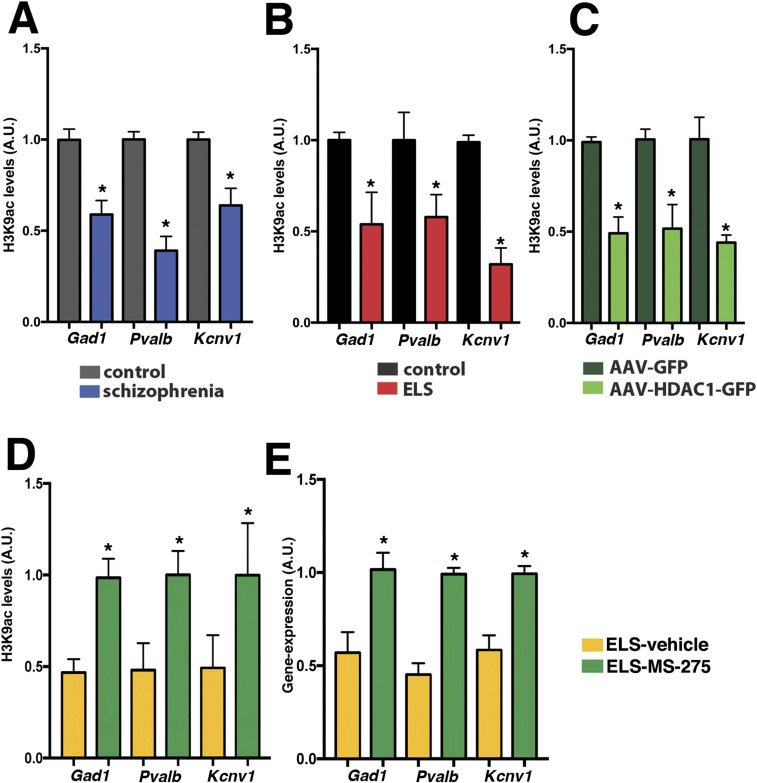
Fig. S9.
H3K9 acetylation is decreased in patients with schizophrenia in response to ELS and HDAC1 overexpression and is ameliorated by MS-275 treatment. (A) ChIP analysis reveals decreased H3K9ac levels at the gene promoters of Pvalb, Gad1, and Kcnv1 in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of patients with schizophrenia compared with controls (n = 8 per group; *P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test). (B) Similar data were obtained in the mPFC of mice subjected to ELS (n = 5) compared with the corresponding control group (n = 5 per group; *P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test). (C) In mice that received AAV-HDAC1-GFP injections, decreased H3K9ac levels (PFC) were observed at the gene promoters of Pvalb, Gad1, and Kcnv1 compared with the HDAC1-GFP group (n = 5 per group; *P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test). Tissue from the ELS and corresponding control group was isolated at PND120. Tissue from AAV-injected mice was harvested 4 wk after injection. (D) ChIP analysis reveals increased H3K9ac at the gene promoters of Pvalb, Gad1, and Kcnv1 when measured in the mPFC of mice subjected to ELS and treated with MS-275 from PND120–140. (n = 5 per group; *P < 0.05 versus vehicle, unpaired Student’s t test). (E) qPCR analysis reveals that Pvalb, Gad1, and Kcnv1 mRNA levels in the mPFC are increased in mice subjected to ELS and treated with MS-275 from PND120–140 compared with the vehicle group (n = 5 per group; *P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test). Error bars indicate SEM.