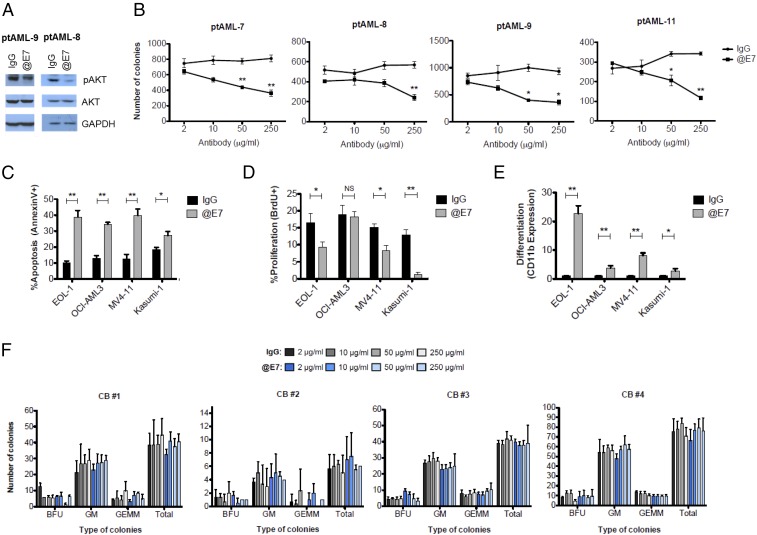
Fig. 5.
EGFL7 inhibition results in decreased human AML cell growth without affecting normal hematopoietic cells. (A) Blasts from AML patients were cultured in SFEM with 10% FBS in the presence of 50 μg/mL of normal human IgG or anti-EGFL7 (@E7) antibody for 1 h. Total proteins were extracted for immunoblotting of pAKT-S473 and total AKT. GAPDH was used as loading control. (B) Human primary blasts (400,000) from AML patients (n = 4) were treated with 2, 10, 50, or 250 μg/mL of IgG control or anti-EGFL7 antibody in SFEM containing 10% FBS and cytokines for 2 h. Twenty thousand cells were plated in triplicate in methylcellulose medium and scored after 14 d of culture for mean ± SD colony numbers. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (C) Forty-eight hours after IgG control vs. anti-EGFL7 antibody treatment (50 μg/mL) of AML cell lines, apoptosis was evaluated by Annexin V/7AAD staining, (D and E) Cell proliferation was measured using BrdU incorporation (D), and differentiation analysis was evaluated by CD11b expression (E). CD11b is depicted as the ratio of the CD11b expression value of the examined sample to the CD11b expression value of the corresponding IgG-treated control. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (F) CD34+ CB cells from four different donors were plated in methylcellulose medium in the presence of increasing concentrations (2, 10, 50, or 250 μg/mL) of human IgG or anti-EGFL7 and were scored after 14 d of culture. Along with total number of colonies, colony types [erythroid burst-forming units (BFU), granulocyte/monocyte (GM), or granulocyte/erythrocyte/monocyte/megakaryocyte colonies (GEMM)] were enumerated also.