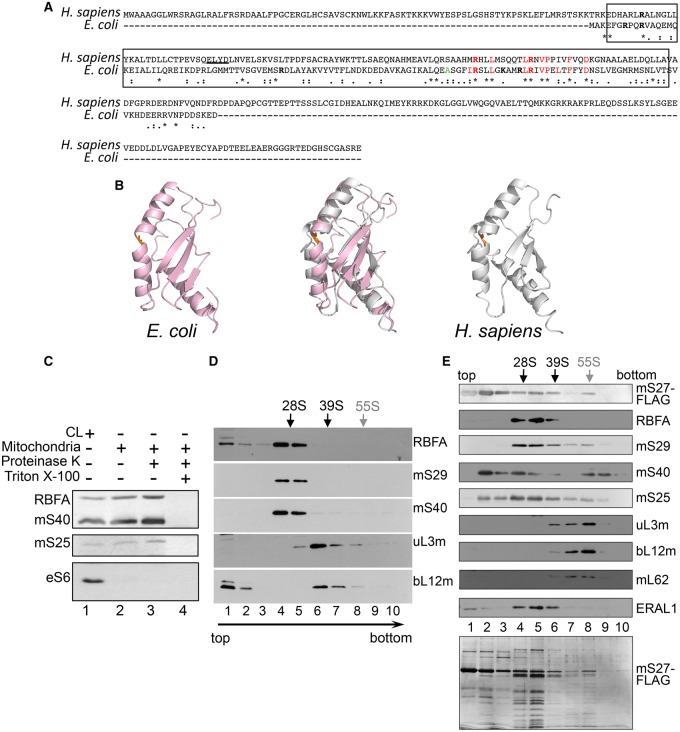
Figure 1. The human orthologue of bacterial RbfA associates with the mitoribosomal SSU.
(A) Amino acid alignment (ClustalW) of RBFA from human (NP_079081.2) and E. coli (P0A7G2) shows identities as (*), high level of similarity by (:) and lower levels by (.). Boxed region indicates the predicted position of ‘ribosome-binding’ and RNA-binding ‘KH’ domains. The basic residues (in bold) Arg7, Arg10, Arg45, Arg80, Lys85 and Arg90 in E. coli RbfA are implicated in RNA binding [21]. Ala75 (orange) forms an inter-helical kink shown in B. A conserved sequence signature (IRXXLXXXXXLRXVPXLXFXXD) is located in the C-terminal region of E. coli RbfA. Human RBFA shares most but not all of these characteristics. (B) NMR-derived structures of E. coli RbfA (pink; PDB 1KKG, [21]) and the corresponding region of human RBFA that excludes the N- and C-terminal extensions (H. sapiens, silver; PDB 2E7G, [53]) are depicted individually and superposed using Coot [31]. Both exhibit type II KH domain folds (three helices and three β-strands). Human RBFA has an additional short helix, underlined in the panel A alignment. The inter-helical kink, formed in E. coli by Ala75 (1KKG) and Ser159 (2E7G) in human, is shown in orange. (C) Lysate (50 µg, lane 1) and mitochondria (10 µg, lanes 2–4) were prepared from HEK293 cells. Isolated mitochondria were treated with proteinase K in the absence (lane 3) or presence (lane 4) of 1% Triton X-100. Western blots detected RBFA, mitochondrial matrix markers (mitoribosomal subunits mS40 and mS25) and a cytosolic marker (cytosolic ribosomal subunit eS6). (D) HEK293 cell lysate (700 μg) was separated through a 10–30% sucrose gradient. Fractions were analyzed by western blot, using antibodies against mt-SSU (mS29 and mS40) and mt-LSU (uL3m and bL12m) components. The positions of the mt-SSU (28S), mt-LSU (39S) and the monosome (55S) are indicated. RBFA distribution was determined using antibodies against the endogenous protein. (E) FLAG-tagged mS27 was expressed, immunoprecipitated and the immunoprecipitate separated by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Fractions were subjected to western blot to detect the monosome, the mt-SSU, and its assembly intermediates (fractions 2–3). A silver-stained gel of the fractions is shown below.