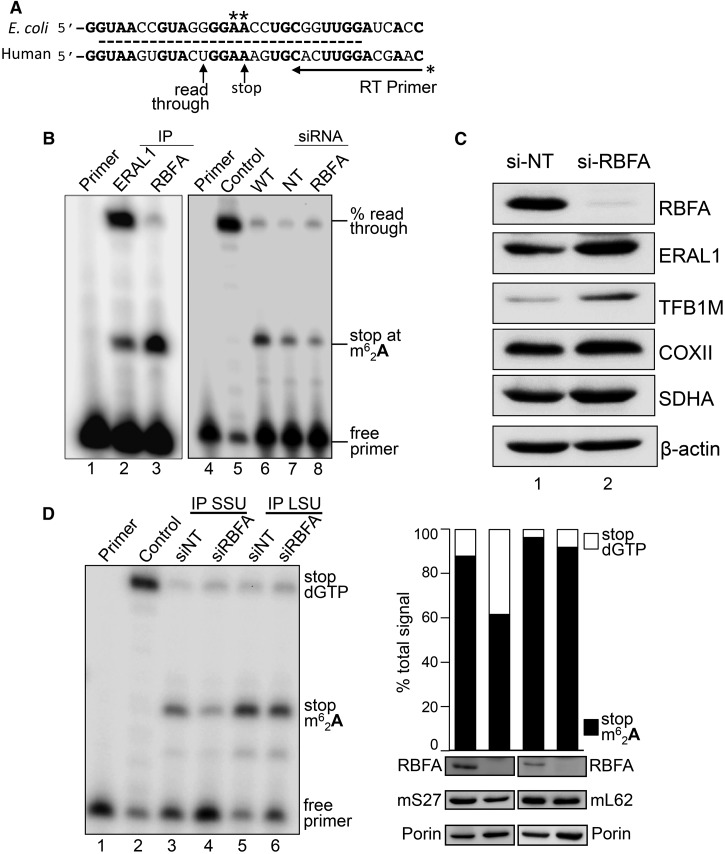
Figure 4. Depletion of RBFA causes a decrease in 12S rRNA modification.
(A) Schematic presenting sequence conservation of helix 45 (dashed line) and the primer extension assay used to measure the modification levels at adenine residues A936/A937 in human 12S rRNA. If the modification is present, the primer extends four residues, and in its absence the primer extends a further five residues. (B) To determine the modification status of 12S rRNA bound to ERAL1-FLAG (lane 2, 3-day induction) or RBFA-FLAG (lane 3, 3 days), these proteins were immunoprecipitated from HEK293 cells and the bound RNA was extracted. Samples were subjected to primer extension and denaturing PAGE. (Right panel) Cells were depleted of ERAL1 (3 days) followed by 4 days of siRNA treatment; si-NT (lane 7) or si-RBFA (lane 8). RNA was extracted and primer extension performed. Primer alone (lane 1, 4), extension on unmethylated template (lane 5) and wild-type cells (lane 6) were controls performed in parallel. (C) Western blot (50 µg of cell extracts) determined the steady-state levels of ERAL1, TFB1M and COXII in cells depleted of RBFA. SDHA and β-actin were used as loading controls. (D) HEK293 cells were grown for 5 days in the presence of NT or RBFA siRNA with induction of mS27-FLAG (IP SSU) or mL62-FLAG (IP LSU) on day 3. (Left panel) Cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation and bound 12S rRNA was assessed by primer extension alongside controls (primer alone, lane 1; unmethylated control, lane 2), and then visualized and quantified as described. (Right panel) Densitometric analysis is presented for lanes 3–6 from the left panel (stop m62A937 = arrested at dimethylation; stop dGTP = full read-through). Western blots of the initial extract (50 µg) are shown probed for RBFA, mS27/mL62 via FLAG and porin.