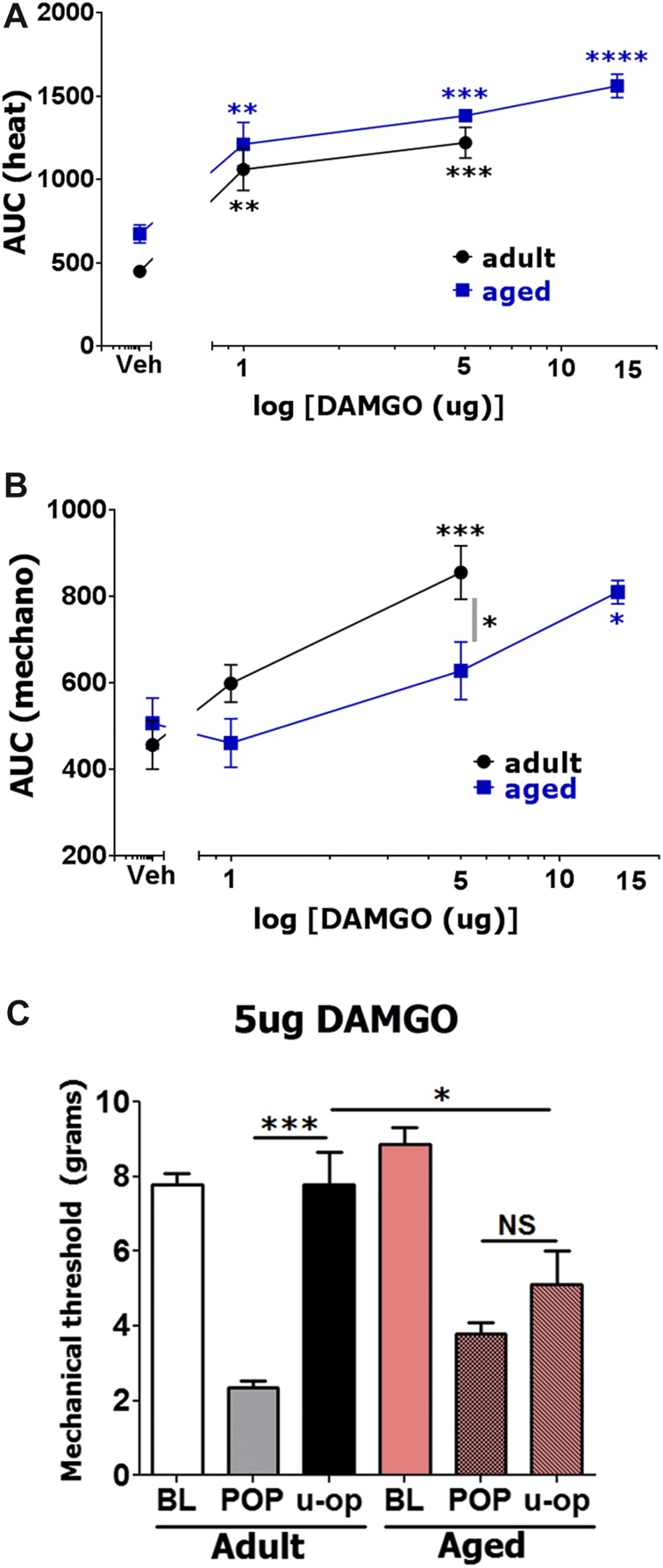
Figure 4.
Effects of spinal injection of DAMGO on postoperative hypersensitivity in adult and aged mice. Incision-induced thermal (A) and mechanical (B) hypersensitivity were generated in adult and aged mice. At 1 day (for adults) and 1 to 3 days (for aged) postsurgery, different dosages of DAMGO were administrated intrathecally, and thermal (A) and mechanical (B) hypersensitivity were measured at 30 and 120 minutes post-DAMGO injection. Data are presented as area under the curve (AUC). Significance within age groups for DAMGO-produced antihypersensitivity was compared against vehicle treatment (1-way ANOVA; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; n = 5–8). Significance between age groups was assessed by 2-way ANOVA. DAMGO dosages are indicated below log x-axis. Veh is vehicle treated conditions. Mouse ages are indicated. (C) Mechanical antihypersensitivity (at 30 minutes post-opioid injection) by spinal administration of 5 μg DAMGO for adult and aged mice (1-way ANOVA; separately for adult and aged mice and 2-way ANOVA between adult and aged mice; NS, nonsignificant; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; n = 5–8). U-op marking below x-axis is DAMGO produced effect.