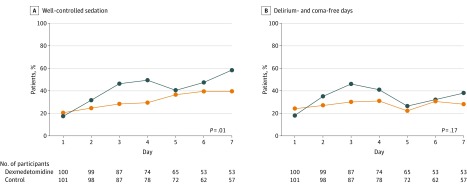
Figure 3. Percentage of Patients With Well-Controlled Sedation and Delirium- and Coma-Free Days During ICU Stay Among the Dexmedetomidine and Control Groups.
To examine the effect of dexmedetomidine on sedation control and the occurrence of delirium and coma, a generalized linear model was used accounting for repeated measurements in the same patient. Well-controlled sedation was defined as a Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS) score between −3 and +1 throughout 1 day spent in the intensive care unit (ICU) and was defined as (rate of controlled sedation) = (patient’s number of days with well-controlled sedation)/(total number of patients in the ICU), calculated for each day. Coma was defined as an RASS score between −4 and −5 throughout 1 day in the ICU. Day 1 is defined as the first day of randomization into the trial.