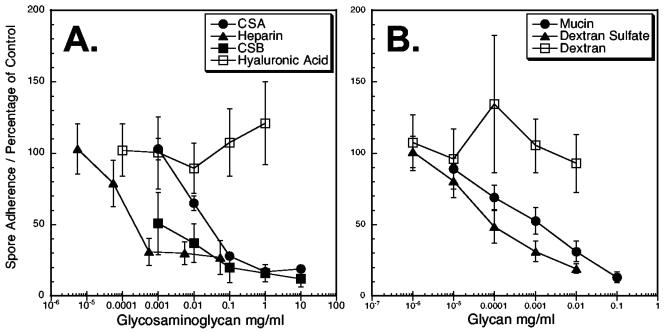
FIG. 3.
E. intestinalis spore adherence is inhibited by exogenous sulfated glycans. An adherence assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods in the presence or absence of various exogenous glycans in 10-fold serial dilutions. The glycans tested as potential inhibitors included the GAGs heparin, chondroitin sulfate A (CSA), chondroitin sulfate B (CSB), and hyaluronic acid (A). The non-GAG glycans tested included type II porcine stomach mucin, dextran sulfate, and dextran (B). After 4 h of incubation of 107 spores with and without the glycan inhibitor, the host cells grown on coverslips were removed and washed to remove unbound spores. The mean number of attached spores was determined for each concentration of potential inhibitor. The percentage of spores inhibited from adherence is shown relative to that of control samples without exogenous glycans. These data represent one of three experiments that were performed with similar results.