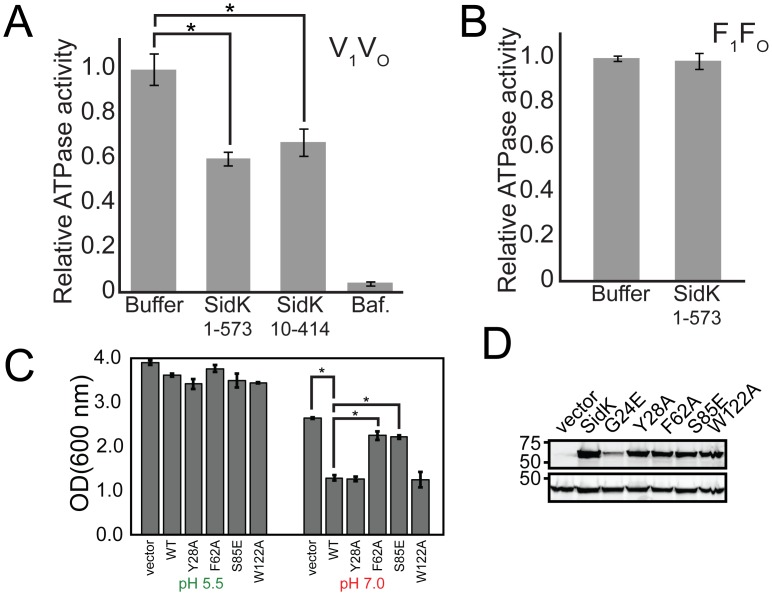
Fig 3. Inhibition of the V-ATPase by SidK.
A, SidK, either full length or residues 10–414, inhibits V-ATPase by approximately 40% with 10× excess of SidK to available binding sites. “Baf.” indicates bafilomycin. B, SidK does not inhibit ATPase activity of the F-type ATP synthase, showing that it is a specific inhibitor of V-ATPases. C, Yeast expressing SidK and SidK point mutations show normal growth on medium at pH 5.5. Wild type SidK reduces yeast growth on medium buffered to pH 7.0, indicating V-ATPase inhibition. SidK point mutations F62A and S85E alleviate SidK inhibition of V-ATPase while point mutations Y28A and W122A do not. D, Western blotting shows that all of the point mutations tested are expressed in S. cerevisae at levels similar to wild type (PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase as a loading control), except G24E, which was consequently excluded from the analysis. *, p<0.01.