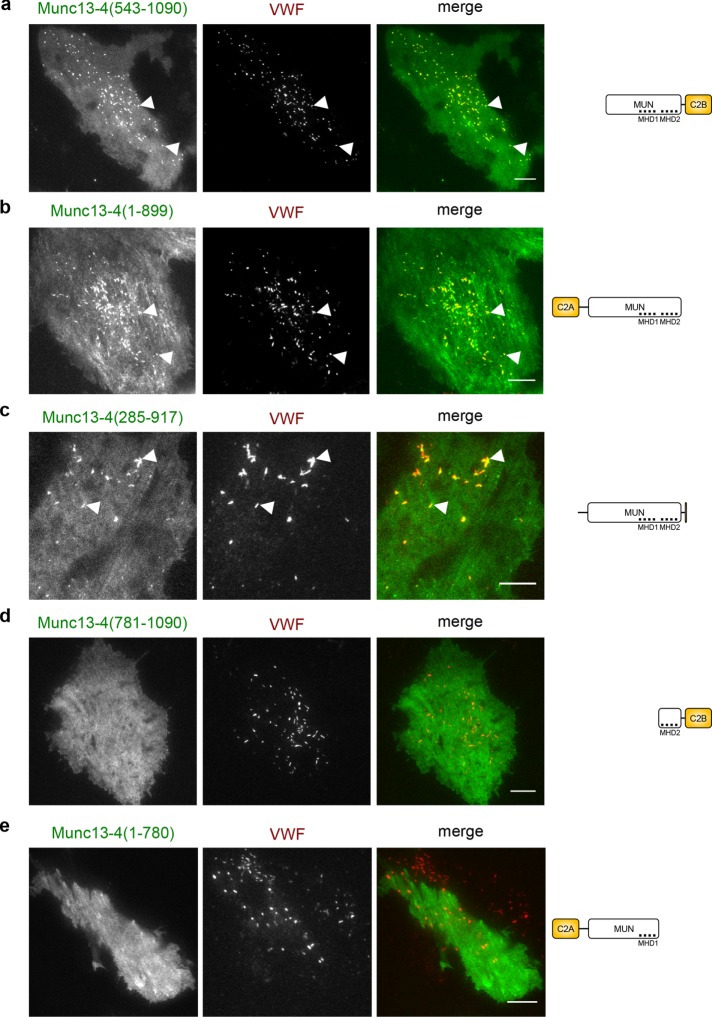
FIGURE 3:
Munc13-4 localizes to WPBs via its MHD1/MHD2 region. TIRF images of live HUVECs expressing different truncated versions of YFP–Munc13-4 and VWF-RFP as WPB marker for 48 h. Right, domain structures of the respective Munc13-4 mutants lacking the C2A (aa 109–284), C2B (aa 904–1047), or parts of the MUN domain (aa 319–901). The first ∼100 aa of Munc13-4 of unknown structure were omitted for simplicity. MHD1 (aa 577–677) and MHD2 (aa 788–894) are two regions within the MUN domain with conserved sequences in all Munc13 proteins. (a) Munc13-4(543-1090), which lacks the C2A and parts of MUN domain but contains the entire region around MHD1/2. (b) Munc13-4(1-899), which lacks the C2B but contains the entire MHD1/2 region. (c) Munc13-4(285-917), which lacks C2A and C2B. (d) Munc13-4(1-780), which is truncated after MHD1 and therefore lacks MHD2-C2B. (e) Munc13-4(781-1090), which lacks the entire N-terminal part including MHD1. Arrowheads mark examples of colocalizations of Munc13-4 and VWF on WPBs. Note that mutants containing the MHD1 and MHD2 regions localize to WPBs, whereas those lacking these sequences do not. Scale bars, 10 µm.