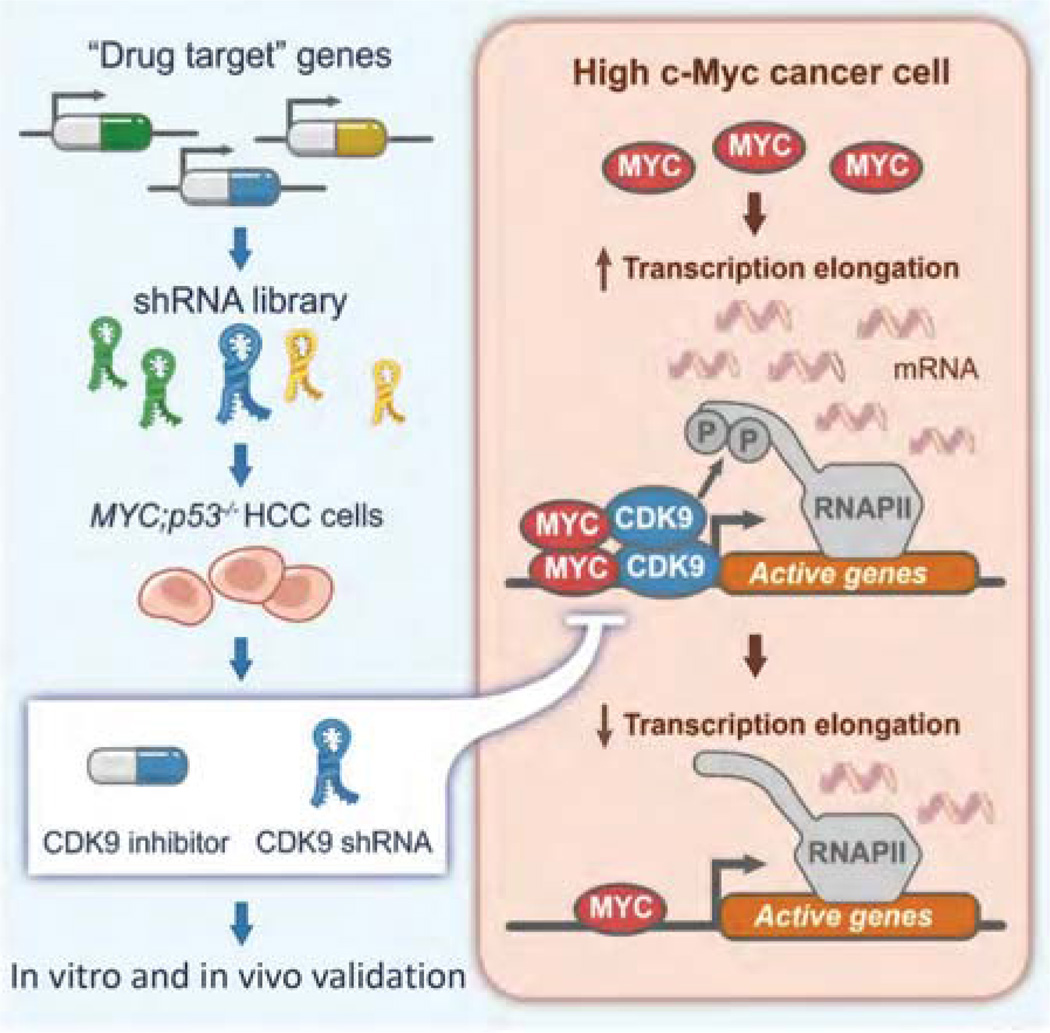
Figure 1.
Schematic of a focused RNAi screen for genes encoding known drug targets. By screening a custom library of short-hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) directed toward known drug targets in a genetically defined Myc-driven hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) model, we identified CDK9—a key component of the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) complex—as required for MYC-overexpressing HCC. Results from shRNA-mediated and pharmacological CDK9 inhibition together highlight the relevance of transcription elongation in the addiction of cancer cells to MYC and suggest that targeting MYC-mediated transcription elongation can be an effective strategy for the treatment of MYC-overexpressing tumors.