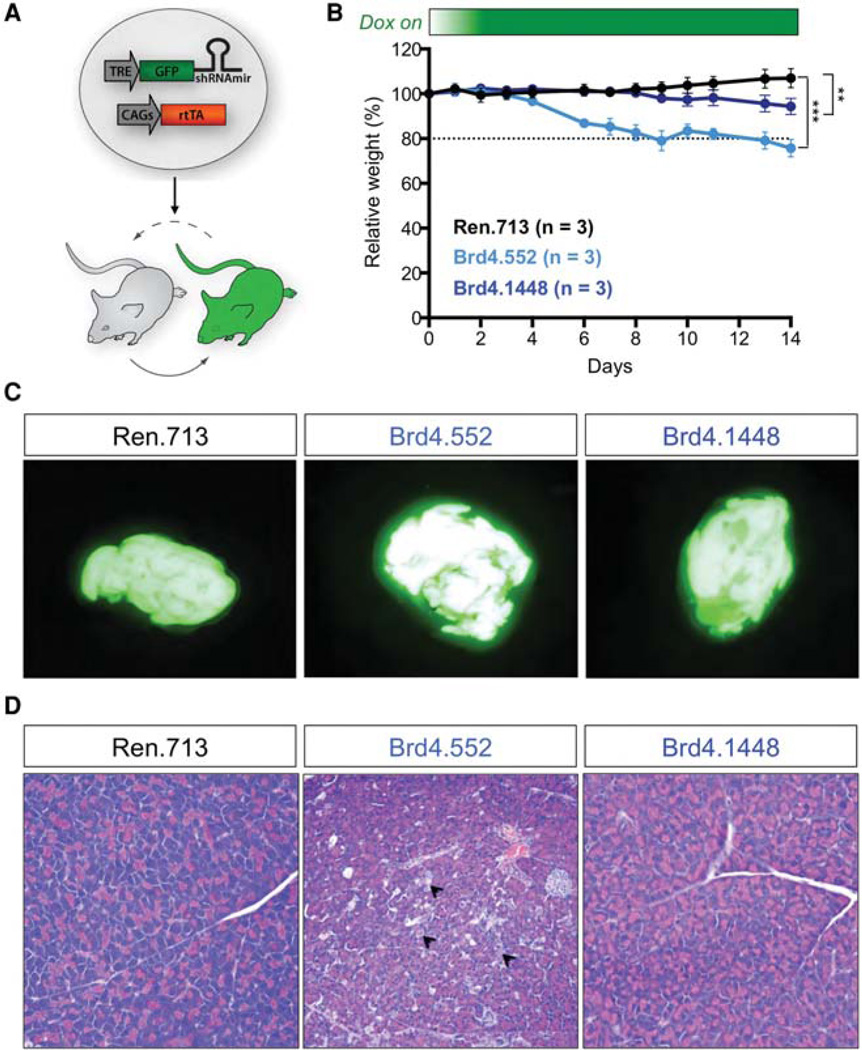
Figure 5.
Inducible and reversible transgenic RNA interference (RNAi) mice for assessing toxicities associated with systemic Brd4 suppression. (A) Schematic representation of the generation and application of short-hairpin RNA (shRNA) transgenic mice. Tetracycline response element (TRE)-driven miR-30 shRNAs are targeted to the ColA1 locus to drive doxycycline (dox)-dependent genes knockdown in embryonic stem cells and embryonic and adult tissues of the mouse as previously described (Bolden et al. 2014). By further using a sensitive and widely expressed rtTA mice strain, CAGs-rtTA3, GFP-miR-30 shRNAs can be efficiently expressed in most tissues to study on-target toxicities. (B) Mean weight changes of male and female (combined) CAGs-rtTA3/+; TG-Ren.713, TG-Brd4.552, and TG-Brd4.1448 mice on dox diet, relative to day 0 of dox treatment. Error bars represent ± SD. (C) Green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression in pancreas from CAGs-rtTA3/+; TG-Ren.713, TG-Brd4.552, and TG-Brd4.1448 mice, maintained on dox diet for 2 wk. (D) Representative hemotoxylin and eosin (H&E) stains of pancreas from CAGs-rtTA3/+; TG-Ren. 713, TG-Brd4.552, and TG-Brd4.1448 mice maintained on dox diet for 2 wk. Arrowheads indicate the extensive scattered acinar cells undergoing necrosis. All mouse experiments were approved by the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol no. 11-06-011). Statistical significance was calculated by two-tailed Student’s t-test (Prism 6 software). Significance values are *, P < 0.05; **, P <, 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001.