Fig. 2.
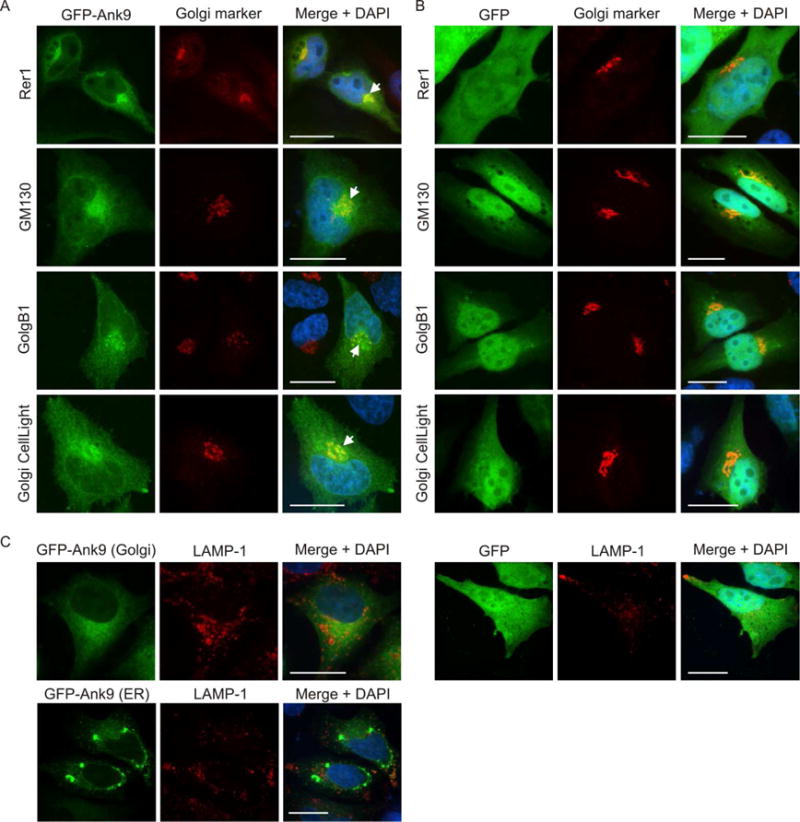
Ectopically expressed Ank9 localizes to the Golgi, but not to lysosomes. HeLa cells expressing GFP-Ank9 (A) or GFP (B) were fixed and screened at 16 h post transfection with GFP antibody and antibody against Rer1 (labels the ER-to-Golgi intermediate compartment and cis-Golgi), GM130 (labels the cis-Golgi), or GolgB1 (labels the cis- and medial-Golgi) prior to examination by confocal microscopy. Transfected cells were also incubated with CellLight Golgi-RFP, which labels the medial- and trans-Golgi, prior to fixation and confocal microscopic analyses. Representative fluorescence images of cells viewed for GFP, Golgi marker, and merged images plus DAPI are presented. White arrows denote representative points of GFP and Golgi marker signal colocalization. Because the cell cycles of the HeLa cells were not synchronized, the timing by which GFP-Ank9 localizes to the Golgi could not be discerned. (C) HeLa cells expressing GFP-Ank9 or GFP were also screened with antibody against LAMP-1, which labels lysosomes. Representative images depicting GFP-Ank9 exhibiting Golgi-like (Golgi) and ER-like (ER) localization patterns, as based on colocalization studies presented in Figure 2A and Figure 1A, respectively, are presented. Results are representative of at least three separate experiments having similar results. Scale bars, 20 μm.
