Figure 1.
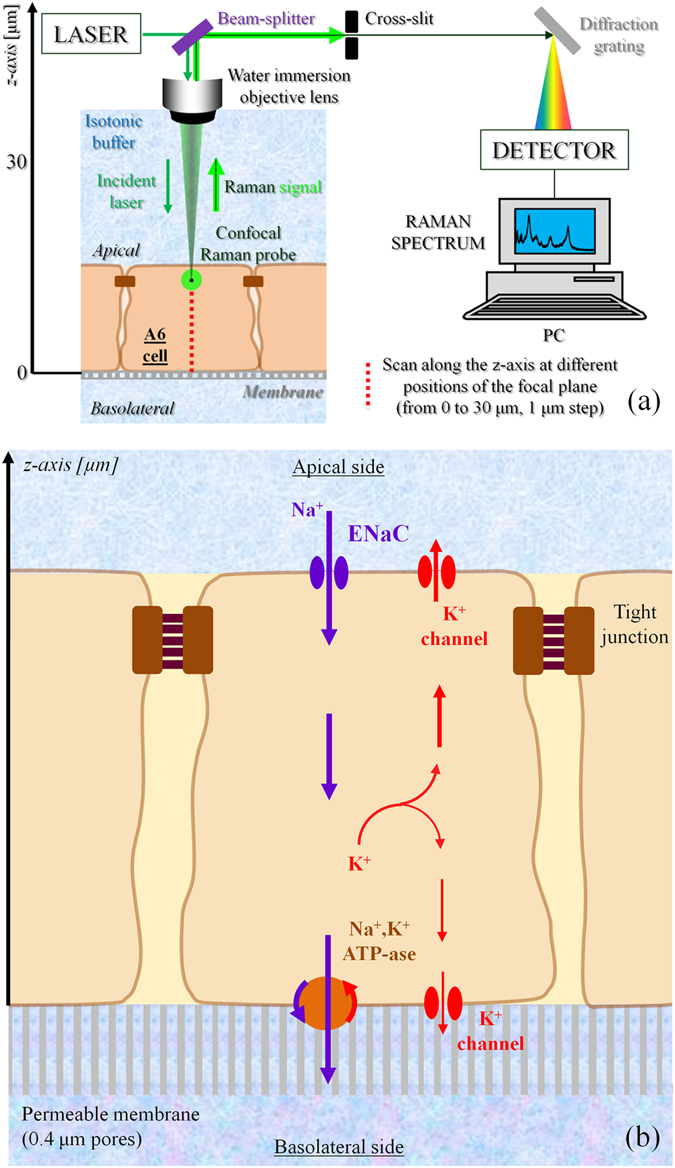
(a) Explanation of the z-axis scanning protocol adopted in the Raman spectroscopy experiments. The incident laser and the back-scattered Raman signal collected by the same lens are separated using a beam splitter. The confocal cross-slit enables to increase the spatial resolution of the measurements by cutting off the signal coming from regions that are more than a few hundred of nm out of the focal plane. A diffraction grating is used to split the light into its components, whose intensities are measured by the detector. (b) Schematic of the A6 renal epithelial cell under investigation, in which are described the ionic transport mechanism of sodium reabsorption.
