Figure 2.
Host Cortical and Rubral Neurons Make Monosynaptic Contact with Graft Neurons
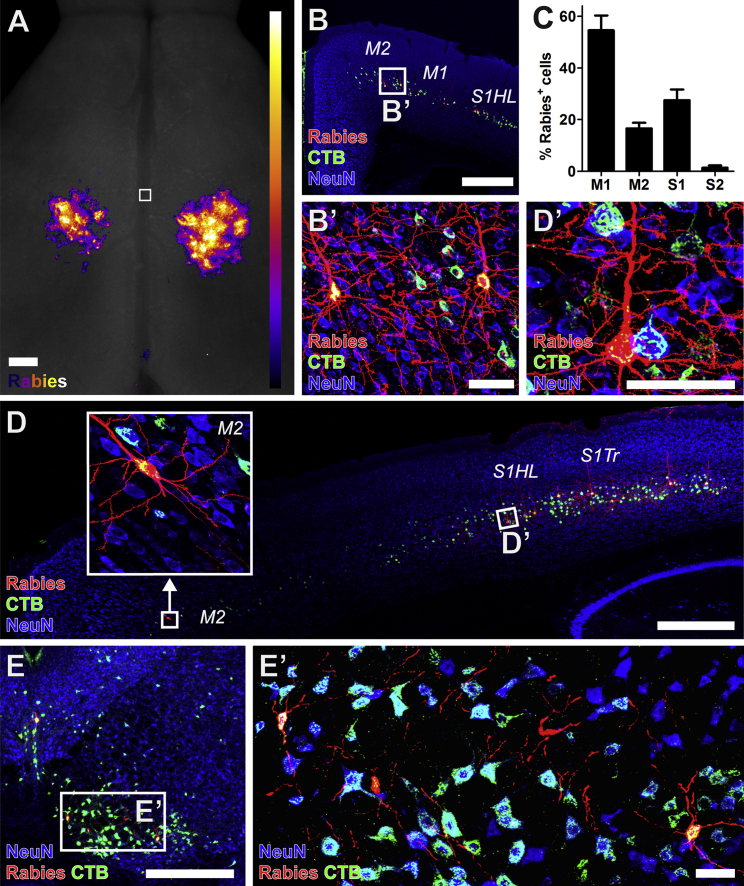
(A) Heatmap of the location of Rabies-mCherry+ corticospinal neurons making monosynaptic contact onto Rabies-Helper spinal NPC graft-derived neurons (aggregate of n = 8 mice). Horizontal view. Square denotes bregma, with rostral at the top of the image. Most of the Rabies-mCherry signals from the apical dendrites of corticospinal neurons are located caudal to the bregma, in the caudal forelimb and hindlimb regions.
(B and C) Rabies-mCherry+ (red) cortical neurons making synaptic contacts onto graft neurons co-labeled with CTB injected into graft sites (green), and were (C) found most frequently in the primary motor cortex (M1; mean of all Rabies-Helper grafted mice cut coronally, ± SEM, n = 5). NeuN, blue.
(D) Rabies-mCherry+ cortical neurons making synaptic contacts onto graft neurons were also found in the secondary motor cortex (M2, boxed detail) in the rostral forelimb area, and hindlimb and trunk primary somatosensory cortex (S1HL, S1Tr).
(E) Rabies-mCherry+ neurons were also present in the red nucleus. 30-μm-thick sections.
Scale bars, 500 μm in (A, B, D, and E) and 50 μm in (B′, D′, and E’). See also Figures S2 and S4.