Figure EV1. A syntaxin1:SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex containing the transmembrane domain of syntaxin1 serves as a labile, yet efficient acceptor for synaptobrevin binding.
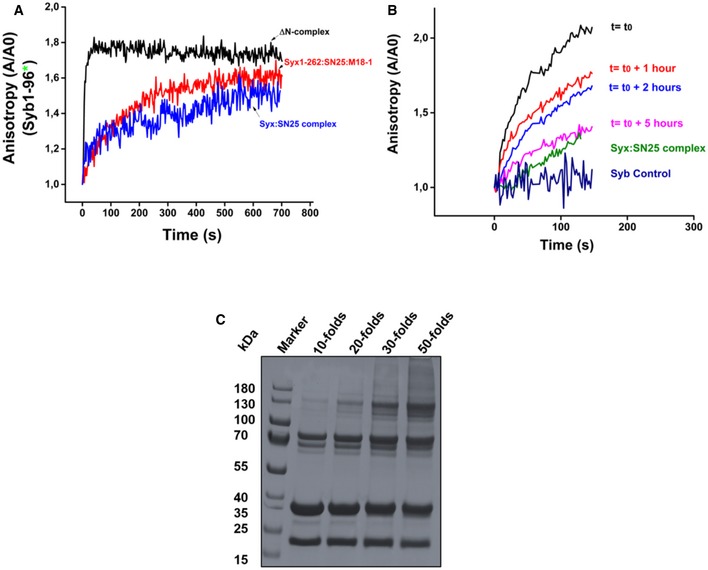
- Binding of synaptobrevin to the syntaxin1 (1‐262):SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex (red curve) was slower as compared to the ΔN complex (black curve) and resembled binding to the binary syntaxin1a:SNAP25 (2:1) complex (blue curve). This was in contrast to the complex containing the transmembrane domain of syntaxin1. Precise time‐point measurements using the syntaxin1 (1‐262):SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex were, however, not performed.
- Binding of fluorescently labeled synaptobrevin (1‐96) to the syntaxin1 (1‐288): SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex was measured over increasing time intervals using fluorescence anisotropy. The complex showed a decrease in the rate of synaptobrevin binding with increasing periods of time.
- The syntaxin1 (1‐288):SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex could be cross‐linked by the chemical cross‐linker BS3. A titration with increasing amounts of the cross‐linker showed that a 50‐fold excess of the cross‐linker was optimum for cross‐linking the syntaxin1:SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex. The “folds” indicate the molar excess of BS3. The cross‐linked band appeared around a molecular weight of 130 kDa.
