Figure 4. Synaptobrevin binding does not displace Munc18‐1 from the syntaxin1:SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex.
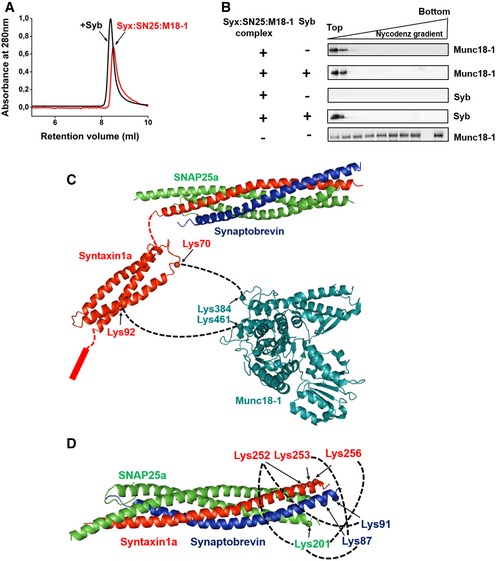
- Gel‐filtration profiles of syntaxin1:SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex with (black curve) or without (red curve) synaptobrevin pre‐incubation. A slight shift in the elution peak toward lower retention volume was observed after incubation of the complex with synaptobrevin. Separation was performed on Superdex 10/300 Increase column (GE Healthcare).
- Syntaxin1:SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complexes were mixed with synaptobrevin and thereafter incorporated into liposomes. The liposomes were then separated from the free (or displaced) proteins using a Nycodenz density gradient; 25 μl fractions were then collected from top to bottom of the gradient and analyzed by Western blotting using α‐Munc18‐1 and α‐synaptobrevin antibodies. As a control experiment, protein‐free liposomes were treated with Munc18‐1 (bottom panel, the second last lane is blank due to the marker position) and processed as above to assess the non‐specific binding of Munc18‐1 to the liposomes.
- Cross‐links observed between syntaxin1 and Munc18‐1 after incubation of the syntaxin1:SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex with synaptobrevin. Freshly purified complex was incubated with synaptobrevin and was subjected to chemical cross‐linking with BS3. MS/MS analysis revealed that Munc18‐1 remains associated with syntaxin1 after SNARE complex formation. Cross‐links were observed between residues lying in the Habc region of syntaxin1 (residues 70 and 92) and K384 and K461 of Munc18‐1, indicating a major conformational shift of syntaxin1 with respect to Munc18‐1 after synaptobrevin addition. No cross‐links were observable between the SNARE motifs of SNAP25 and Munc18‐1
- MS/MS analysis of the cross‐linked samples after synaptobrevin treatment also revealed cross‐links between the C‐termini of syntaxin1, SNAP25, and synaptobrevin, thereby demonstrating the formation of a fully zippered SNARE complex after synaptobrevin binding to the syntaxin1:SNAP25:Munc18‐1 complex.
Source data are available online for this figure.
