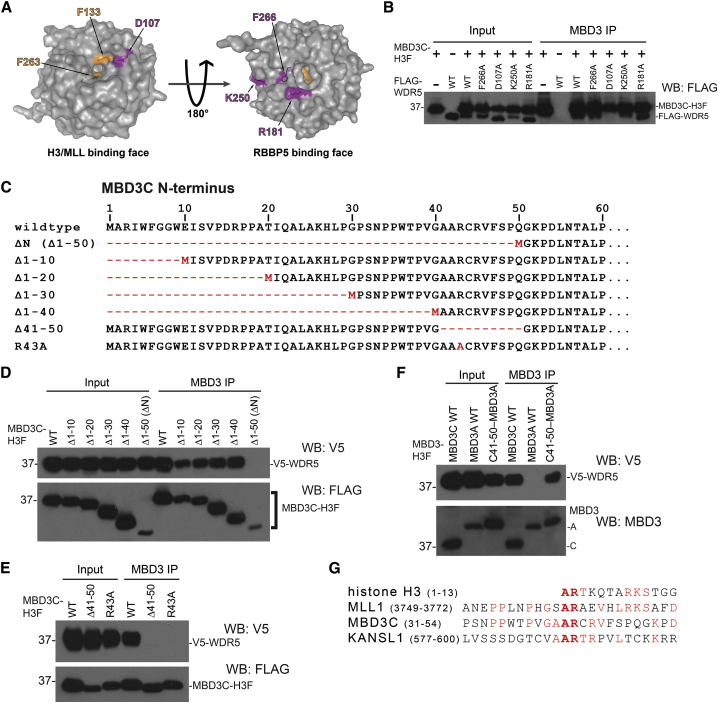
Figure 2.
The WDR5 Histone H3 Binding Pocket Is Required to Bind MBD3C
(A) PyMol depiction of WDR5 crystal structure (PDB: 2GNQ) showing the H3K4/MLL1 (left) and RBBP5 (right) binding pockets. Residues individually mutated to alanine (Yang et al., 2014) are shown in magenta. Residues necessary for MLL1 R3761 or histone H3 R2 binding are shown in orange.
(B) CoIPs with MBD3 antibody from 293T cells co-transfected with expression vectors carrying MBD3C-H3F and indicated FLAG-tagged WDR5 mutants.
(C) Schematic of Mbd3c N-terminal mutant constructs used in (D) and (E).
(D–F) CoIPs with MBD3 antibody in 293T cells performed as in (B), using V5-tagged WDR5 constructs and H3F-tagged MBD3 constructs. For “C41-50−MBD3A,” MBD3C amino acids 41–50 were fused to the N terminus of the MBD3A isoform.
(G) Alignment of the MBD3C N terminus with WDR5-binding regions of mouse MLL1, KANSL1, and histone H3.