Figure 4.
Transfer of EV-Encapsulated MicroRNAs Propagates GBM Heterogeneity
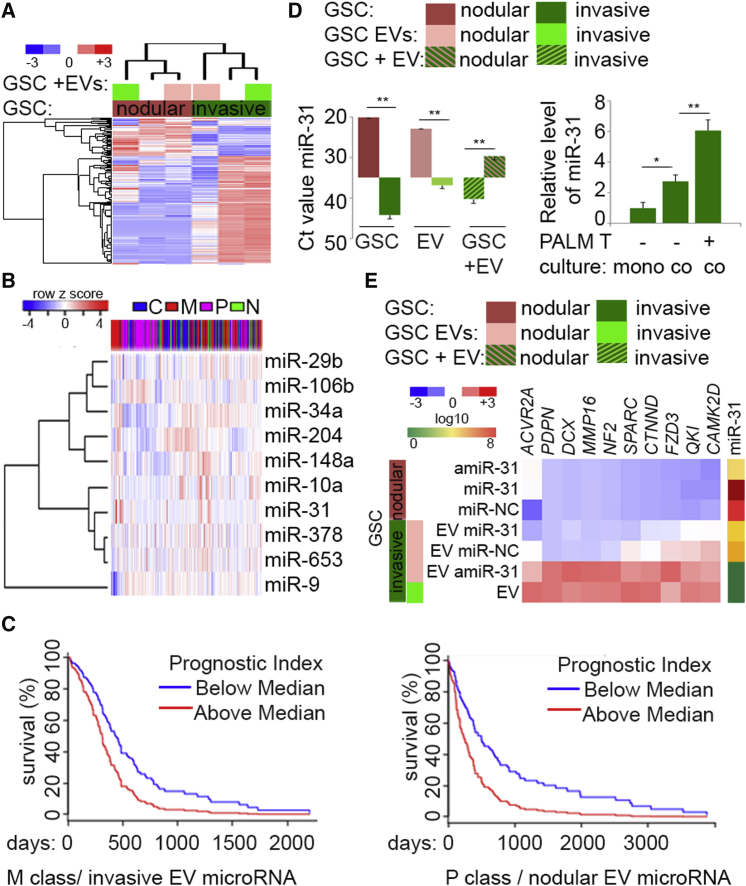
(A) Exchange of EV between distinct GSCs shifts subpopulation-specific microRNA signatures. Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of expression of 307 microRNAs in non-treated GSCs (n = 4 independent GSCs, n = 2 per subclass) and EV-treated GSCs (n = 4 independent EVs, n = 2 per subclass) is shown.
(B) MicroRNAs upregulated upon EV uptake are diversely expressed in GBM. MicroRNA sets that are coherently upregulated in nodular and invasive GSCs (n = 4 independent GSCs, n = 2 per subclass) upon treatment with EVs (p < 0.05, fold >2) were queried with TCGA-classified GBM dataset and identified by clustering with subtype prediction. C, classical; M, mesenchymal; P, proneural; N, neural.
(C) Survival analysis in mesenchymal (left) and proneural (right) GBM subtypes based on the impact of the prognostic index of multiple microRNAs (miR-148a, miR-204, miR-34a, miR-106b, and miR-9 [left], and miR-31, miR-653, miR-378a, miR-29b, and miR-10a [right]) based on retrospective data extrapolated from the TCGA. For mesenchymal GBM (n = 125 patient samples), log-rank p = 0.004, Prognostic Index hazard ratio = 1.83, p = 0.004. For proneural GBM (n = 112 patient samples) log-rank p = 0.001, Prognostic Index hazard ratio = 2.09, p = 0.001.
(D) MiR-31 is EV-transferred between GSC subpopulations. Left: qPCR analysis of miR-31 in donor nodular GSCs (n = 3 independent GSCs), their EVs (n = 3 independent GSC EVs), and recipient invasive GSCs (n = 3 independent GSCs). Right: monoculture spheroid of GFP-tagged invasive GSC (mono-) and co-culture spheroids of GFP-tagged invasive GSCs and PALM-Tomato (PALM T) nodular GSCs were sorted for GFP-positive (co-culture negative) or double-positive (GFP and Tomato [co-culture positive]). Data (n = 3 independent experiments) are shown as the mean raw Ct value ± SD, ∗∗p < 0.01 (left); and as mean ± SD, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 (right).
(E) EV-miR-31 targets subclass GSC-specific genes. Nodular GSCs (n = 3 independent GSCs) were transfected with control (NC), microRNA mimic (miR-31), and microRNA inhibitor (amiR-31) (top three rows), and invasive GSC were treated with EVs derived from such nodular GSCs or their own EVs (n = 3 independent GSCs). qPCR analysis of selected targets and miR-31 is shown as hierarchical clustering and log10 assessed based on the value of expression, respectively.
See also Figure S4.