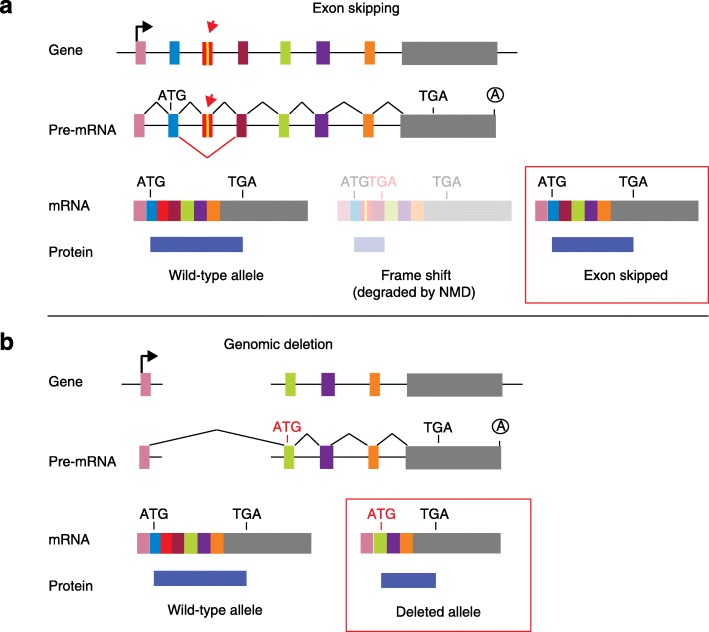
Fig. 1.
Two mechanisms for exon skipping. a Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)-induced indel (red arrow) results in the intended mRNA with a premature termination codon subject to nonsense-mediated decay (NMD), but skipping the mutated exon retains the reading frame and produces an aberrant protein. b CRISPR-induced genomic deletion removes three exons, including the translation initiation codon, such that a downstream internal ATG produces a protein that is truncated at the N-terminus. Red boxes indicate mRNAs that produce aberrant proteins