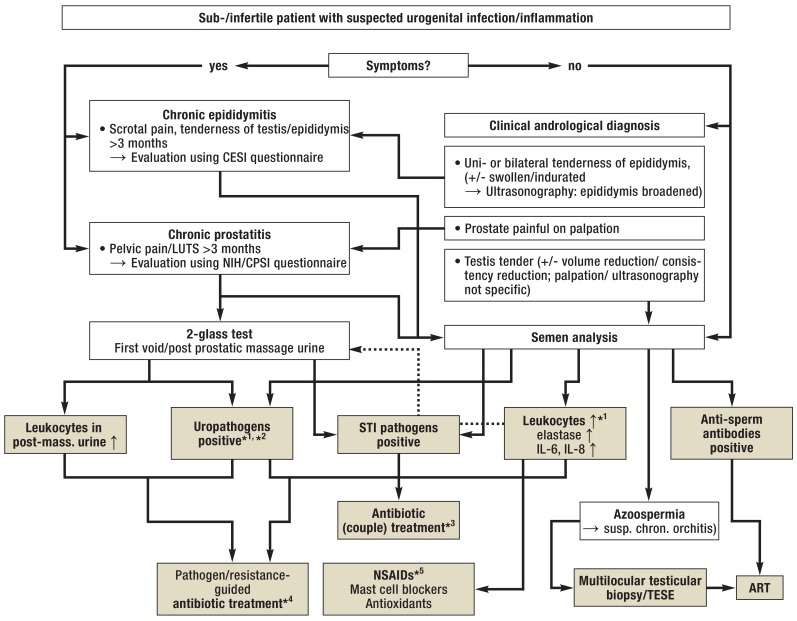
Figure 2.
Algorithm for the management of urogenital infections/inflammation in men with infertility
*1 In case of isolated findings: Confirmation by follow-up examinations; in case of increased levels of inflammatory markers in the ejaculate: advanced diagnostic assessment (2-glass test)
*2 Bacterial count in the ejaculate >103 CFU/mL, for urine samples see Figure 1
*3 Always antimicrobial therapy with co-treatment of partner according to guideline recommendations; cycle-adapted administration/contraception to prevent negative effects on early pregnancy (37, 38, e46)
*4 In case of symptom-free patients with positive inflammatory markers in the ejaculate (see Table 2): Treatment only in case of significant bacterial count and positive confirmatory test (see above; [e1, e2]); treatment duration 2 to 4 weeks, subject to pathogen/indication and medication (with the exemption of azithromycin; WARNING: current warnings for fluoroquinolones [e57]; tentative antibiotic treatment, e.g. in patients with non-significant bacterial count/isolated signs of inflammation, is not indicated). Because of the risk of negative effects on spermatogenesis/sperm function: Follow-up ejaculate testing or use of ART only after a treatment-free interval (several weeks) (cf. [22]).
*5 In case of sign of inflammation in the ejaculate (see Table 2), primarily without pathogen detection/after antibiotic treatment: Administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; e.g. diclofenac [100–150 mg/d] or equivalent medications, including cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors; treatment duration 3–6 weeks); mast cell blocker, if needed; subsequent adjuvant treatment with antioxidants (e.g. vitamin E) optional.
ART, assisted reproductive technology (with TESE: in-vitro fertilization with intracytoplasmic sperm injection; IVF/ICSI); CESI, chronic epididymitis symptom index (e58); CPSI, chronic prostatitis symptom index (e40); CFU, colony-forming units; LUTS, lower urinary tract symptoms; NIH, National Institute of Health; STI, sexually transmitted infections; TESE, testicular sperm extraction; ↑, increased