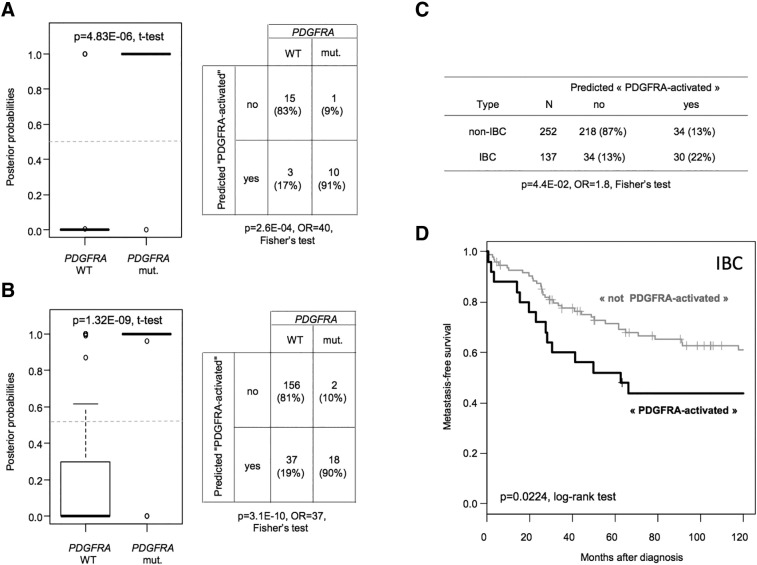
Figure 1.
Generation of a robust predictive model for PDGFRA activation in GIST and application to breast cancer samples. (A) Classification of 29 GIST samples from the learning set (Ostrowki's set). (Left) Box-plot showing the distribution of posterior probabilities, according to our predictive model, of presence of PDGFRA mutation in samples without (“WT”) and with (“mut.”) PDGFRA mutation. (Right) Cross-table between the observed PDGFRA status (“mut.” versus “WT”) and the predicted PDGFRA activation status according to our model. (B) Similar to A but applied to the validation series of 213 GIST samples. (C) Cross-table between the predicted “PDGFRA-activated” status and the clinical phenotype (IBC versus non-IBC) of 137 IBC samples and 252 non-IBC samples collected through the IBC International Consortium gene expression data set. (D) Kaplan-Meier MFS in patients with IBC according to the predicted PDGFRA activation status: “activated” (black curve) versus “not activated” (gray curve). The respective 5-year MFSs were 52% and 72%.