Figure 4. Ent protects against neutrophil-mediated bacterial killing.
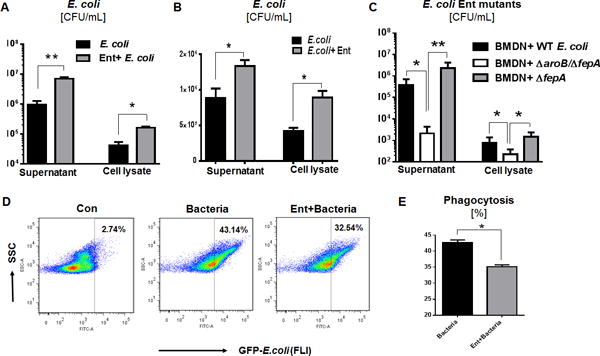
(A) Neutrophil-mediated bacteria killing assay in presence of exogenous Ent (25 μM) with WT E. coli. (B) PMNs-mediated bacteria killing assay in presence of exogenous Ent (25 μM) with WT E. coli. (C) WT E. coli and its isogenic mutants employed in the killing assay to assess the effect of endogenously-derived Ent. (D and E) Phagocytosis (%) was determined by flow cytometric analysis of opsonized GFP-expressing E. coli by neutrophils. In vitro assays were performed in triplicates and are representative of two independent mouse experiments. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. * p< 0.05, ** p<0.01, and *** p<0.001.
