Figure 6. Ent chelates cytosolic labile iron pool (LIP) in neutrophils and mitigates their anti-microbial functions.
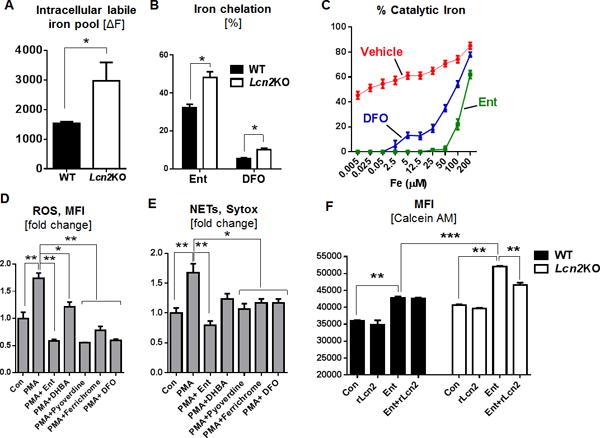
BMDNs from Lcn2KO mice and their WT littermates were incubated with Ent. (A) Cytosolic LIP was quantitated using the Calcein-AM based flow cytometry method. (B) Bar graphs represent the % intracellular iron chelation by Ent and DFO in Lcn2KO and in WT neutrophils. (C) Line graphs showing the effects of Ent and DFO in quenching the bleomycin-based LIP detection assay. Influence of other microbial siderophores on the basal and PMA-induced (D) ROS generation and (E) NETs formation in WT BMDNs. (F) Bar graphs represent the intracellular LIP by Calcein-AM assay using Ent and rLcn2 in Lcn2-deficient and WT BMDNs. MFI= Mean fluorescence intensity. In vitro assays were performed in triplicates and are representative of two independent mouse experiments. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. * p< 0.05, ** p<0.01, and *** p<0.001.
