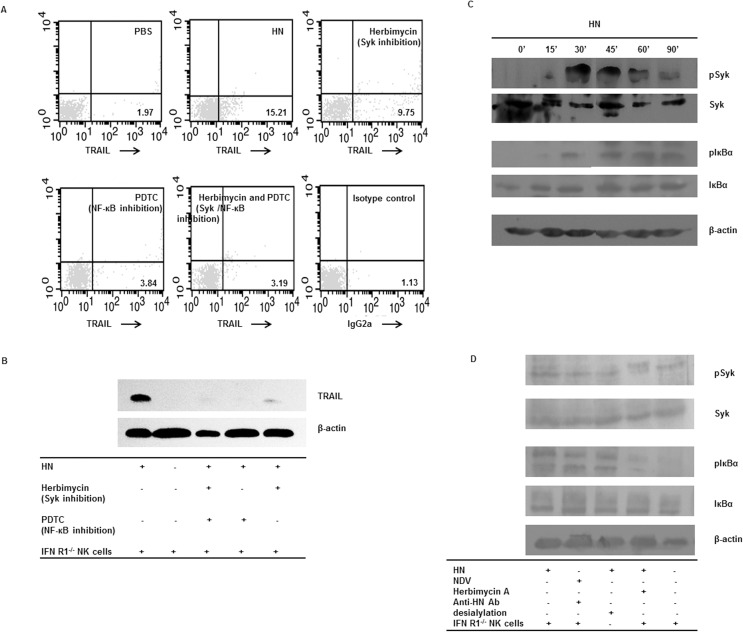
Fig 4. The correlation between TRAIL upregulation and Syk, NF-κB pathways in IFN-R1-/- NK cells.
(A) HN-induced TRAIL expression in NK cells was mediated by spleen tryosine kinases (Syk) and NF-κB pathways. Purified murine splenic IFN-R1-/- NK cells were pre-cultured with herbimycin A or PDTC, and then incubated with soluble recombinant NDV HN. Cells were stained with a PE-conjugated mAb against TRAIL. PBS-treatment NK cells were used as negative controls. (B) Cellular proteins were extracted and subjected to western blotting with a mAb against TRAIL. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Phosphorylation of Syk and IκBα in HN-induced IFN-R1-/- NK cells. Purified IFN-R1-/- NK cells were incubated with recombinant NDV HN for 15, 30, 45, 60, and 90min. Cellular proteins were extracted, and Syk, phosphorylated Syk (pSyk), IκBα, and phosphorylated IκBα (pIκBα) were detected by western blotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. (D) Purified IFN-R1-/- NK cells were pre-cultured with the sodium salt of N-acetylneuraminic acid, 2,3-dehydro-2-deoxy, or herbimycin A, prior to incubation with HN or a mixture NDV 7793 and neutralizing antibodies against HN. Cellular proteins were extracted, and Syk, pSyk, IκBα, and pIκBα were detected by western blotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. Results are representative of three independent experiments using different mice.