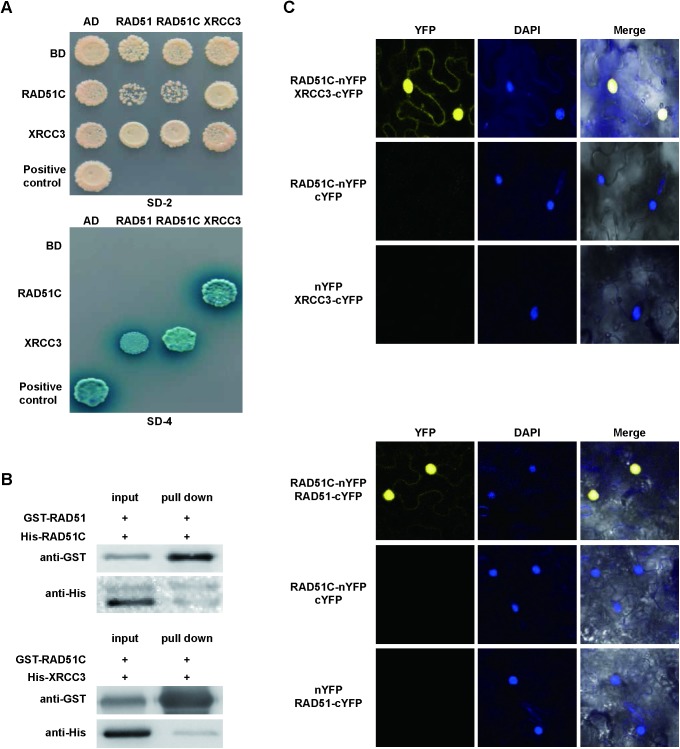
Fig 3. AtRAD51C interacts with AtRAD51 and AtXRCC3 in vitro and in vivo.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid assay showing AtXRCC3 interaction with AtRAD51 and AtRAD51C. The known DYT1-DYT1 interaction is used as a positive control [82]. AD refers to the activation domain, BD refers to the DNA-binding domain, SD-2 refers to SD-Leu-Trp and SD-4 refers to SD-Leu-Trp-His-Ade+X-gal. Blue indicates a positive interaction. (B) Pull-down assay showing that AtRAD51C interacts with AtRAD51 and AtXRCC3. (C) BiFC assay in tobacco cells showing strong nuclear signals for AtRAD51-AtRAD51C and AtRAD51C-AtXRCC3 interactions. Left panels are yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) signals, middle panels are nuclei stained with 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), and right panels merge the DAPI-stained images with the YFP signals and bright field images.